Subscribe for our newsletter to have the latest stories and curated art recommendations delivered straight to your inbox
Exploring Pop Art: Definition, Movement, and Notable Artists
RTISTIQ TEAM
 Like
Like comments
comments SAVE
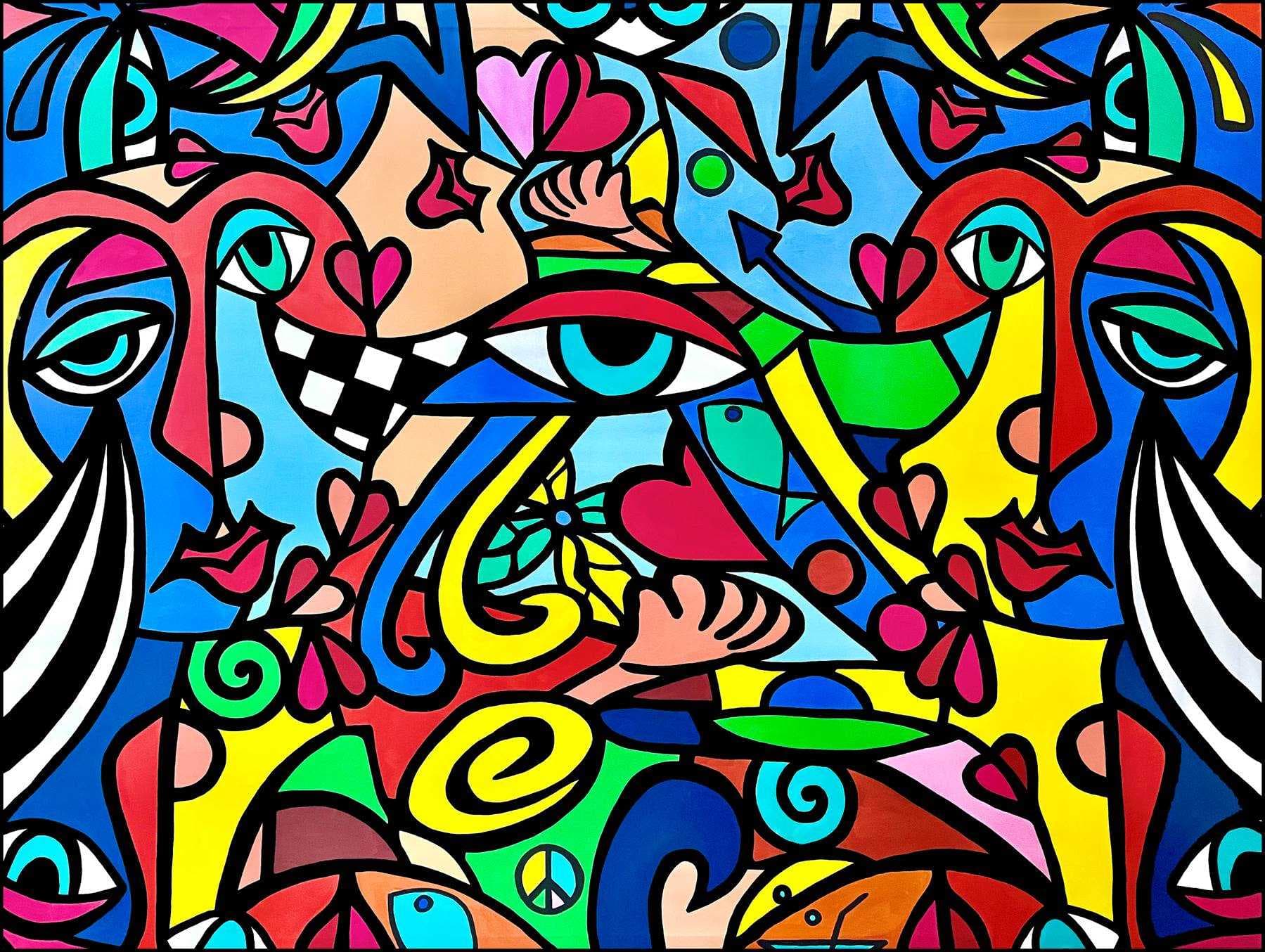
SAVEPop Art emerged as a vibrant and influential artistic movement in the mid-1950s, challenging traditional notions of art and embracing the popular culture of the time. With its bold imagery, vibrant colors, and incorporation of everyday objects, Pop Art brought art closer to the masses. This article explores the definition, key characteristics, notable artists, and lasting impact of Pop Art on the art world and popular culture.
What is Pop Art?
Pop Art, short for "popular art," was a movement that emerged in the United States and the United Kingdom during the 1950s and 1960s. It was a reaction against the dominant abstract expressionist movement, which focused on subjective, introspective, and non-representational art. Pop Art, on the other hand, celebrated the ordinary, the commercial, and the mundane, drawing inspiration from mass-produced consumer goods, advertising, and popular culture.
What are the characteristics of Pop Art?
- Appropriation and Repetition: Pop Art often incorporated images and objects taken from popular culture, such as product packaging, comic books, and celebrities. Artists manipulated and repeated these images to highlight their significance and challenge the concept of originality.
- Bold Colors and Simplified Forms: Pop artists used vibrant, eye-catching colors to attract attention and evoke a sense of consumerism. They simplified forms and employed graphic techniques, reminiscent of advertising and comic book aesthetics.
- Irony and Critique: Pop Art often conveyed a sense of irony and critique by juxtaposing disparate elements, subverting traditional art forms, and challenging societal norms. It questioned the boundaries between high and low culture, art and mass production, and the commercialization of society.
Leading Artists of the Pop Art Movement
Andy Warhol: One of the most iconic figures associated with Pop Art, Warhol employed screen-printing techniques to reproduce everyday objects, such as Campbell's soup cans and Coca-Cola bottles. His work explored themes of consumerism, fame, and the cult of celebrity.
Roy Lichtenstein: Lichtenstein is renowned for his comic book-inspired paintings, featuring bold lines, Ben-Day dots, and speech bubbles. By appropriating and enlarging comic strip panels, he elevated popular culture to the realm of high art.
Claes Oldenburg: Oldenburg's sculptures took ordinary objects and transformed them into monumental works of art. His oversized sculptures of hamburgers, typewriters, and clothespins challenged the viewer's perception of scale and materiality.
Richard Hamilton: Considered the father of British Pop Art, Hamilton explored the relationship between art and technology. His collage-like works incorporated images from advertising, cinema, and popular magazines, reflecting the media-saturated society.
Impact and Legacy
Pop Art's influence extends far beyond its initial emergence in the 1960s. Its vibrant and accessible style has had a lasting impact on contemporary art, design, fashion, and popular culture. Pop Art paved the way for subsequent art movements such as Neo-Pop, Street Art, and the appropriation art of the 1980s. It blurred the boundaries between high and low art, challenged the traditional notions of artistic value, and emphasized the democratization of art.
Concluding Remarks
Pop Art revolutionized the art world by breaking away from the abstract and introspective tendencies of the time. It celebrated the everyday, the commercial, and the popular culture, making art more accessible to a wider audience. Through its use of appropriation, bold colors, and irony, Pop Art continues to captivate and inspire, leaving an indelible mark on contemporary art and popular culture.
Explore our Curated Collections
SIMILAR ARTICLES

Singapore Art and Artists: Exploring the Rich Cultural Tapestry and Creative Expression
Singapore is a vibrant city-state that has a thriving arts and culture scene. Over the years, Singapore has seen the emergence of numerous talented artists who have made significant contributions to the local and international art scene. In recent years, the art scene in Singapore has experienced significant growth and development, further solidifying its position as a vibrant cultural hub. Here's a glimpse into Singapore's art and artists: Art Movements in Singapore: Compared to European and other Asian counterparts, Art is relatively young in Singapore and driven mainly by the many cultures and traditions that make up Singapore society. What makes Singaporean Art more distinct is the merging of Chinese, Malay and European Art forms with a blend of localised cultural heritage, indigenous beliefs and popular practices in Singapore. Here is an overview of the key periods and milestones in the history of visual art in Singapore: Early Art Influences (Pre-19th Century): Before the 19th century, Singapore was primarily a trading port, and the cultures of the Malay Archipelago, China, India, and the West predominantly influenced art. Traditional art forms, such as batik, sculpture, and calligraphy, were practised by local artisans. Colonial Influence (19th-early 20th century): The arrival of British colonial rule in the 19th century brought Western influences to Singapore. European artists and art teachers introduced academic art practices, such as oil painting and portraiture, to local students. Notable artists during this period include Raffles Institution founder Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles and his wife, Sophia Raffles. Nanyang Style and Cultural Identity (mid-20th century): In the 1950s, a significant art movement known as the Nanyang Style emerged in Singapore. Led by four master artists of the time, Liu Kang, Chen Wen Hsi, Georgette Chen and Cheong Soo Pieng, this movement combined Chinese ink painting techniques with Western art styles, creating a distinctive fusion. The Nanyang Style was a form of cultural expression exploring the identity of the Southeast Asian region and its people. Modern Art Society (mid-20th century): In the 1960s, the Modern Art Society was established, advocating for modern art practices and promoting local artists. This period marked a shift towards experimentation and exploring abstract and conceptual art forms. Artists like Lim Yew Kuan and Anthony Poon were instrumental in driving the development of modern art in Singapore. Contemporary Art and Global Recognition (late 20th century-present): In the late 20th century, Singapore's art scene continued to evolve and embrace contemporary art practices. The opening of institutions like the Singapore Art Museum (SAM) in 1996 and the National Gallery Singapore in 2015 provided platforms for local and international contemporary artists. Singapore's participation in international art events, such as the Venice Biennale and the Singapore Biennale, further propelled its global recognition. Most Notable Artists of Singapore Singapore has been home to many prominent Artists continuously gaining International reputations. Here are some of the most notable and significant artists from the city-state of Singapore Georgette Chen (1906-1993) was a Chinese-born Singaporean painter known for her realistic portraits and landscapes. She is considered one of the pioneers of modern art in Singapore and a key figure of the "Nanyang School" of Art. She had spent much of her early life in China, France and New York, before making Singapore her home in the year 1954 to spend later years of her life. GEORGETTE CHEN, BOATS AND SHOPHOUSES , (credit: Sotheby's) Chen Wen Hsi (1906-1991) was a Chinese-born Singaporean painter known for his lyrical landscapes and portraits. Similar to other prominent artists Chen Wen Hsi, had spent a good part of his life in China before making Singapore his permanent home. He along with four other prominent artists founded the Nanyang Style of Painting in the year 1953, creating a watershed moment for the Singapore Art scene. In 1964 he was awarded with the "Public Service Star" award. One of his paintings "Two Gibbons Amidst Vines", addorns the back of every $50 note of Singapore. The gibbons are there not only to beautify the note but they also signify a great artist who contributed his entire whole life to the art world. Cheong Soo Pieng (1917-1983) was another prominent Chinese-born Singaporean painter known for his abstract paintings. He along with Chen Wen Hsi, Georgette Chen and Liu Kang founded the Nanyang style of art, one of the most important movements of Singapore's cultural History. After migrating to Singapore in 1946, he took up Art teaching at the Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts, and began his fervent amalgamation of Western and Chinese pictorial styles. Best known for his stylized depictions of Malay and Balinese women, he worked in a unique aesthetic that blended Hindu, Chinese, and Modernist European influences. Lim Tze Peng (born 1921) is a Singaporean painter known for his Chinese ink paintings. He is considered one of the most influential artists of his generation in Singapore. His masterpieces have been exhibited in many local and international exhibitions and prominent art centers in Singapore, including the Singapore Art Museum and Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts.. Hundred and two years old Mr Lim currently is the oldest living Artist of Singapore and was awarded the Cultural Medallion in 2003 for his vast contributions to the Art and Culture of the Country. LIM TZE PENG (courtesy South China Morning Post) Amanda Heng (born 1951): Amanda Heng is a contemporary artist known for performing art and installations. She often addresses issues of gender, identity, and social norms in her works and has exhibited her art internationally. She rose to pominance in the 1990's and is considered a pioneer of Performance Arts in Singapore. She is among the first Singaporean Artists to win the distinguished Benesse Prize and also awarded Cultural Medallion for Visual Arts in 2010. Among the many firsts that she brought to the Art scene in Singapore, includes the founding of the Artists Village in 1988 and then later in 1999 she formed the Women in The Arts (WITA) Collective, the first Artists run collective in Singapore. Tan Swie Han (born 1943) Born in Indonesia Tan Swie Han is a Singaporean multi-disciplinary Artist who migrated from Indonesia in 1946 and is known for his Chinese calligraphy and Contemporary Art Sculptures. He is also distinguished as being the most expensive artist in Singapore after he sold his painting "Moon is Orbed" for S$3.7M in the year 2012 and later again broke his own record by selling his ink on rice-paper artwork "Bada Shanren" for S$4.4M. Tan Swie Han (courtesy Straits Times) Yeo Shih Yun (born 1976): Yeo Shih Yun is a Singaporean artist known for her abstract ink paintings. She combines traditional Chinese ink painting techniques with contemporary approaches, creating bold and expressive artworks reflecting her experiences and emotions. Jane Lee (born 1963): Jane Lee is a contemporary artist known for her experimental approach to painting. She often uses unconventional materials such as epoxy paint and polyurethane foam to create textured and multi-dimensional artworks that challenge traditional notions of painting. Lee has toyed with the painting structure to create rich and tactile abstract works that frequently combine two into three dimensions. These are just a few examples of the many talented artists from Singapore who have significantly contributed to the local and international art scene. The art scene in Singapore continues to evolve and grow, with new artists constantly emerging and pushing the boundaries of artistic expression. Head on to our curated collection Inspired-By-Singapore with a selection of works created by Artists worldwide that could illustrate different sides of Singapore's cultural diversity. Part of this collection is a selection of paintings by the Australian artist Dean O'Callaghan painted and inspired by Singapore's cityscapes and exclusively available on RtistiQ.

Exploring Visual Art Styles You Should Know: A Quick Snapshot
Art is a vast and diverse realm that encompasses a wide range of styles and movements. Each art style represents a unique approach to creative expression, influenced by historical, cultural, and artistic contexts primarily originating in Europe and later in United States, but had influences and impacts beyond the continent. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore 20 Visual art styles that have shaped the artistic landscape, from ancient to contemporary times. Understanding these styles will deepen your appreciation and knowledge of art history and provide a foundation for exploring the rich tapestry of artistic endeavors. Renaissance Art (14th-17th Centuries): The Renaissance period witnessed a revival of classical ideals and a focus on naturalistic representation. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael created works that emphasized proportion, perspective, anatomical accuracy, and a sense of idealized beauty. Renaissance art marked a significant shift from the religious and symbolic art of the Middle Ages. Renaissance art not only transformed the artistic landscape but also had a profound impact on Western culture as a whole. It laid the foundation for future artistic movements and continues to inspire and influence artists to this day. The legacy of Renaissance art serves as a testament to the timeless beauty and enduring power of human creativity. Raphael’s Renaissance masterwork The School of Athens, 1511. Via Musei Vaticani Baroque Art (17th-18th Centuries): Baroque art emerged in the 17th century and was characterized by grandeur, dramatic lighting, and ornate details. Artists such as Caravaggio and Gian Lorenzo Bernini created dynamic compositions that conveyed a sense of movement, emotional intensity, and theatricality. The art of this period often featured dramatic, swirling forms, rich colors, and intricate details. Baroque artists employed techniques such as chiaroscuro to create a sense of depth and dramatic contrast. Religious themes remained prominent, with grandiose depictions of biblical scenes and saints, reflecting the influence of the Catholic Church. Whether in painting, sculpture, or architecture, Baroque art sought to engage the senses, create a sense of awe, and convey the power and majesty of the subjects depicted. The Martyrdom of St Matthew by Caravaggio, 1600, in Contarelli Chapel, Rome Neo-Classicism (Late 18th-Early 19th Century): Neo-Classicism revived the classical ideals of ancient Greece and Rome, emphasizing harmony, balance, and idealized forms. Artists like Jacques-Louis David and Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres drew inspiration from classical mythology, history, and literature, seeking to convey noble and moral themes.Neo-Classical artists idealized the human form, drawing from classical sculpture to portray figures with anatomical accuracy and a sense of idealized beauty. Neo-Classicism represented a return to classical ideals and a rejection of the excesses of the preceding artistic styles. It emphasized order, balance, and rationality, celebrating the timeless beauty of classical art while reflecting the cultural and political climate of its time. Giovanni Paolo Panini, “Ancient Rome,” 1757. Image via Wikimedia Commons. Realism (19th Century): Realism emerged in the mid-19th century as a reaction against romanticism and sought to depict subjects with accuracy and fidelity to detail. Artists focused on portraying the everyday, mundane aspects of life, often exploring social issues and reflecting the realities of the time. Notable realist painters include Gustave Courbet and Jean-François Millet. Realism often delved into social issues and political realities, shedding light on the harsh conditions of the working class and critiquing societal norms. Realist artists focused on ordinary people, everyday activities, and common landscapes, highlighting the beauty and significance of the mundane. Realism laid the foundation for subsequent art movements like Impressionism and social realism, influencing the direction of art in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Stonebreakers by Gustave Courbet, 1849, via Phaidon Press Impressionism (Late 19th Century): Impressionism revolutionized the art world in the late 19th century. Artists such as Claude Monet, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, and Edgar Degas sought to capture the fleeting effects of light and atmosphere, using loose brushwork and vibrant colors. Impressionist works often depicted scenes of leisure, landscapes, and urban life. Impressionists explored the changing qualities of light and shadow, capturing the effects of light on different surfaces and objects. Their compositions often featured unconventional framing, cropped viewpoints, and a sense of spontaneity. The advent of photography influenced their compositional choices and encouraged a focus on the immediacy and spontaneity of the moment. Impression Sunrise by Claude Monet in 1872 Pointillism (Late 19th Century): Pointillism, developed by Georges Seurat and Paul Signac, involved the use of small dots or points of pure color to create the illusion of form and depth. The technique relied on the viewer's eye to blend the dots of color optically, resulting in vibrant and luminous paintings. Pointillist artists created their works by applying small dots of pure color to the canvas, which were then blended by the viewer's eye. The juxtaposition of different colored dots produced optical color mixing, creating vibrant and luminous effects. Pointillism was influenced by Impressionism, but it took the exploration of light and color to a more systematic and calculated level. Paul Signac (1863-1935), Capo di Noli, 1898, oil on canvas Art Nouveau (Late 19th-Early 20th Century): Art Nouveau embraced organic forms, flowing lines, and intricate patterns inspired by natural elements. This style influenced various art forms, including painting, architecture, and design. Artists like Gustav Klimt and Alphonse Mucha incorporated curvilinear motifs and stylized representations of flowers, plants, and female figures. Artists embraced new materials like iron, glass, and ceramic, combining traditional craftsmanship with modern techniques. Art Nouveau celebrated beauty, artistic expression, and a departure from historical styles, setting the stage for later modernist movements. Gustav Klimt, Portrait of Adele Bloch-Bauer I, 1907 Expressionism (Late 19th-Early 20th Century): Expressionism sought to convey the emotional and psychological aspects of the human experience. Artists like Edvard Munch, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, and Egon Schiele used distorted forms, intense colors, and gestural brushwork to express inner turmoil and explore the darker aspects of the human psyche. Artists employed vigorous and gestural brushwork, emphasizing the raw and spontaneous execution of their artworks. Expressionism sought to delve into the depths of human emotions and explore the complexities of the human condition. The Scream by Edvard Munch (1893) Fauvism (Early 20th Century): Fauvism, led by artists such as Henri Matisse and André Derain, emerged in the early 20th century. Fauvist artists used bold, non-naturalistic colors to express emotions and evoke an immediate response. The movement rejected traditional representation and emphasized the use of color as an independent and expressive element. Fauvists embraced spontaneity and freedom in their brushwork, rejecting academic constraints and embracing raw and gestural techniques. They aimed to evoke emotions and convey the artist's subjective experience, rather than objective reality. Artists explored the emotional and symbolic potential of color juxtapositions, experimenting with the interaction of hues. 'The Roofs of Collioure', 1905 by Henri Matisse Dadaism (Early 20th Century): Dadaism emerged during World War I as a reaction against societal conventions and the horrors of war. Artists such as Marcel Duchamp and Hannah Höch employed irony, absurdity, and ready-made objects to challenge established norms and question the nature and purpose of art itself. Dadaists embraced absurdity, irrationality, and nonsensical elements in their artworks, seeking to disrupt established modes of thinking. They incorporated everyday objects and ready-mades into their artworks, questioning the concept of originality and challenging the distinction between art and ordinary objects. Dadaism paved the way for later artistic movements, including Surrealism and Conceptual Art. Fountain, 1917 by Marcel Duchamp (1964 Replica by Tate) Cubism (Early 20th Century): Pioneered by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, Cubism challenged traditional perspectives by presenting objects from multiple viewpoints simultaneously. Cubist artworks deconstructed forms into geometric shapes and fragmented planes, emphasizing the two-dimensional nature of the canvas. Analytical Cubism and Synthetic Cubism were two major phases within this movement. They analyzed the subject matter, reducing it to basic geometric forms to explore its essence and underlying structure. They incorporated elements of collage, using materials like newspaper clippings, fabric, and other found objects to add texture and depth to their works. Cubism sought to engage the viewer intellectually, inviting them to interpret and decipher the fragmented forms and multiple perspectives. Glass on table by Georges Braque in 1909 Surrealism (Early 20th Century): Surrealism emerged as a literary and artistic movement in the early 20th century, influenced by the writings of Sigmund Freud. Surrealist artists, including Salvador Dalí, René Magritte, and Max Ernst, aimed to unleash the power of the subconscious mind. They created dreamlike and often bizarre compositions, juxtaposing seemingly unrelated elements to provoke emotional and psychological responses. Artists employed techniques like automatic drawing and spontaneous painting to bypass conscious control and access the subconscious. They questioned societal norms and challenged conventional notions of reality, often blending the ordinary with the extraordinary. Surrealists used symbolic motifs, dreamscapes, and strange transformations to evoke a sense of mystery and provoke emotional responses. The Lovers, 1928 By Rene Magritte Abstract Art (20th Century): Abstract art encompasses a wide range of styles that do not attempt to represent recognizable forms or subjects. Artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Piet Mondrian sought to convey emotions, ideas, or spiritual concepts through non-representational imagery. Abstract art relies on shapes, colors, lines, and textures to evoke a response from the viewer. Abstract artists used color for its emotive and symbolic qualities, often employing bold and unconventional color choices to evoke mood and provoke responses. Artists employed gestural and expressive brushstrokes, layering paint and creating texture to add depth and visual interest to their works. Abstract art invited viewers to interpret and engage with the artwork based on their own perceptions and emotions, emphasizing individuality. Flying Home No 1 by Bea Garding Schubert Abstract Expressionism (1940s-1950s): Abstract Expressionism marked a shift towards non-representational art and emphasized the expression of emotions and ideas. Artists like Jackson Pollock, Willem de Kooning, and Mark Rothko used bold brushwork, gestural movements, and vibrant colors to convey intense emotional states. This movement became synonymous with the post-World War II American art scene. IN_ADAPTE 11 2021 by META MARICARMEN HERNANDEZ Pop Art (1950s-1960s): Pop Art emerged as a reaction to the mass consumer culture of the 1950s and 1960s. Artists such as Andy Warhol, Roy Lichtenstein, and Claes Oldenburg incorporated everyday objects, advertisements, and popular culture references into their works. They employed techniques of reproduction, bold colors, and irony to critique and celebrate the influence of mass media and consumerism. Pop Horizons by Barron Holland Minimalism (1960s-1970s): Minimalism sought to strip art down to its essential elements, often reducing forms to simple geometric shapes and emphasizing clean lines and neutral colors. Artists like Donald Judd, Dan Flavin, and Agnes Martin rejected personal expression and focused on the purity of form and the viewer's direct experience with the artwork. Photorealism (1960s-1970s): Photorealism aimed to create paintings or drawings that closely resemble high-resolution photographs. Artists such as Chuck Close and Richard Estes employed meticulous attention to detail, precise brushwork, and a focus on capturing everyday scenes and objects with astonishing realism. Trocadero 2021 by AGNES LEFEVRE Graffiti Art (20th-21st Centuries): Graffiti art has its roots in street culture and has evolved into a recognized art form. It encompasses various styles, techniques, and messages. Street artists employ spray paint, stencils, and bold lettering to create public murals, tags, and social commentaries. Banksy and Jean-Michel Basquiat are notable graffiti artists who have gained international recognition. Expectation 2021 by SAUNDRA FLEMING Contemporary Art (Late 20th Century-Present): Contemporary art refers to the art being created in the present time and encompasses a diverse range of styles and approaches. It reflects the current socio-political climate, technological advancements, and cultural shifts. Contemporary artists employ various mediums, techniques, and concepts to challenge conventions, explore new ideas, and engage with the complexities of our modern world. Conclusion: Exploring different visual art styles allows us to appreciate the breadth and depth of human creativity throughout history. Each style represents a unique artistic approach, influenced by historical, cultural, and artistic contexts. From the realism of the 19th century to the contemporary experiments of today, these art styles have shaped the course of art history and continue to inspire and challenge artists and art enthusiasts alike. By delving into these visual art styles, we can develop a deeper understanding and appreciation of the diverse and dynamic world of art.
Understanding the Distinction: Contemporary Art vs Modern Art
Over several centuries, Art has evolved with various movements and styles shaping its rich history. Two terms that often confuse people are "contemporary art" and "modern art", more in the context that the words Contemporary and Modern are used interchangeably to mean something in-trend now. While these terms may seem interchangeable, they refer to distinct periods and artistic approaches in the world of art. This article will explore the distinction between contemporary and modern art, shedding light on their characteristics, influences, and significance. Modern Art A Historical Breakthrough Modern Art refers to the period of art that emerged in the late 19th century and prevailed until the mid-20th century. It departed from traditional artistic conventions and embraced innovative techniques, materials, and subject matters. Modern artists sought to challenge established norms and explore new ways of representing the world. One crucial characteristic of Modern Art is its emphasis on experimentation and formal innovation. Artists like Pablo Picasso, Wassily Kandinsky, and Henri Matisse revolutionized art through abstract forms, vibrant colours, and the deconstruction of perspective. They rejected the idea of art solely imitating reality and instead focused on conveying emotional and psychological states. Moreover, modern art was influenced by historical events and societal changes. The impact of World War I, industrialization, and rapid urbanization fueled the desire for artistic expressions that reflected the tumultuous times. Movements such as Cubism, Fauvism, and Surrealism emerged, each with its unique style and thematic focus. Contemporary Art Reflections of the Present In contrast, contemporary art encompasses the artistic practices and expressions of the present time. It emerged in the mid-20th century and continues to evolve as new ideas and technologies emerge. Unlike modern art, Contemporary Art does not adhere to a specific style or movement but embraces diversity and individuality. One defining feature of contemporary art is its inclusivity and openness to various mediums, such as installation, video art, performance, and digital art. Artists like Ai Weiwei, Yayoi Kusama, and Banksy expand the limits of traditional artistic norms and engage with social, political, and cultural issues. Contemporary Art often challenges the viewer's perception, prompting them to question societal norms and ideologies. Another significant characteristic of contemporary art is its global nature. With the advent of technology and globalization, artists have greater access to diverse cultural influences and artistic practices. This has led to a rich tapestry of creative expressions that transcend geographical boundaries and reflect our world's interconnectedness. Conclusion While contemporary art and modern art share a timeline, they are distinct in their approach, style, and influences. Modern Art, emphasizing experimentation and formal innovation, revolutionized the world of Art during the early 20th century. It responded to its time's social and cultural changes and challenged conventional artistic practices. On the other hand, Contemporary Art reflects the artistic expressions of the present moment. It embraces diversity, inclusivity, and new mediums and technologies. Contemporary artists explore a wide range of themes, often engaging with societal issues and pushing the boundaries of traditional art forms. By understanding the differences between Contemporary Art and Modern Art, we can better appreciate the unique contributions of each period and gain a deeper insight into the ever-evolving world of Art. Cover image via Paul Cheng (United States) - Heavy Rain Street
ARTICLES ON ART 101

ART 101
Art Deco Styles: An Iconic Fusion of Elegance and Modernity
Art Deco is a prominent design style that emerged in the 1920s and flourished until the outbreak of World War II. Characterized by its luxurious materials, geometric forms, and streamlined aesthetic, Art Deco became a symbol of glamour and sophistication during the interwar period. This design movement impacted various visual arts, architecture, fashion, and interior design aspects. This article will delve into the captivating world of Art Deco styles, exploring its origins, key characteristics, influential artists and architects, and its lasting legacy. Origins and Influences Art Deco drew inspiration from various sources, blending elements from different cultures, historical periods, and artistic movements. The style's name derives from the 1925 Exposition Internationale des Arts Décoratifs et Industriels Modernes held in Paris, where it was first showcased. However, its roots can be traced back to the early 20th century, influenced by the avant-garde art movements of the time, such as Cubism and Fauvism. One of the significant influences on Art Deco was the discovery of King Tutankhamun's tomb in 1922, which sparked a craze for Egyptian motifs and symbolism. This fascination with ancient Egypt led to incorporation of pyramids, sphinxes, hieroglyphics, and other Egyptian-inspired motifs into Art Deco designs. Additionally, the style's streamlined forms and angular geometry were influenced by the emerging field of industrial design and the aesthetic of machines. Key Characteristics Art Deco is characterized by distinct visual features that make it instantly recognizable. Here are some key characteristics of Art Deco styles: Geometric Shapes: Art Deco embraces geometric shapes, such as zigzags, chevrons, triangles, and stepped forms. These shapes are often used to create dynamic, visually striking compositions. Streamlined Silhouettes: Inspired by the sleek lines of modern technology and transportation, Art Deco features streamlined, aerodynamic silhouettes. These can be seen in the period's buildings, furniture, and even fashion designs. Luxurious Materials: Art Deco celebrates luxury and opulence, employing exotic woods, marble, chrome, glass, and precious metals like gold and silver. These lavish materials contribute to the overall sense of elegance associated with the style. Decorative Elements: Art Deco designs often incorporate elaborate decorative elements, such as sunbursts, stylized floral motifs, and geometric patterns. These decorative details add a touch of sophistication to the overall composition. Bold Colors: Art Deco embraces bold, contrasting colour schemes. Vivid hues like royal blue, emerald green, ruby red, and vibrant yellow are frequently used to create a visually striking impact. Sunburst Motifs: The sunburst motif, symbolizing energy and optimism, is a recurring theme in Art Deco designs. It is often represented as a radiating pattern of geometric lines or a stylized sun. Influential Artists and Architects Numerous artists and architects played significant roles in shaping and popularizing Art Deco styles. Here are a few key figures: Tamara de Lempicka: A prominent Art Deco painter, de Lempicka's works epitomize the style's elegance and glamour. Her portraits often featured fashionable, confident women in luxurious settings. Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann: Ruhlmann was a renowned French furniture designer who created exquisite Art Deco pieces. His furniture designs combined luxurious materials with precise craftsmanship and sleek silhouettes. Erté: A Russian-born artist and designer, Erté was renowned for his extravagant fashion illustrations and costume designs. His work showcased the epitome of Art Deco elegance and sophistication. Raymond Hood: An influential architect, Hood's designs include the iconic Rockefeller Center in New York City. He incorporated Art Deco elements into the skyscraper's design, contributing to the style's popularity in the United States. Clarice Cliff: A British ceramic artist, Cliff revolutionized the pottery industry with her bold and colourful Art Deco designs. Her pottery pieces featured geometric patterns and vibrant glazes. Legacy and Modern Interpretations Although the heyday of Art Deco was in the early 20th century, its influence and appeal continue to resonate in modern design. Art Deco elements can be found in contemporary architecture, interior design, and fashion. In architecture, buildings like the Chrysler Building in New York City and the Napier Municipal Theatre in New Zealand exemplify the enduring impact of Art Deco. These structures continue to captivate audiences with their sleek lines, decorative details, and innovative use of materials. In interior design, Art Deco-inspired furniture and decor remain highly sought after. The style's emphasis on luxury and glamour translates well into modern homes, with its sleek lines and geometric patterns adding a touch of sophistication to any space. Art Deco influences can be seen in the designs of many contemporary fashion houses. The use of bold colours, geometric patterns, and luxurious materials harkens back to the elegance and allure of the Art Deco era. Conclusion Art Deco styles represent a fascinating fusion of elegance and modernity. Emerging in the 1920s, this design movement embraced geometric shapes, luxurious materials, and bold colours. Its influence extended to various artistic fields, leaving an indelible mark on architecture, interior design, fashion, and more. With its timeless appeal, Art Deco continues to captivate audiences and inspire contemporary design. The legacy of this iconic style serves as a testament to its enduring popularity and artistic significance.

ART 101
Exploring Pop Art: Definition, Movement, and Notable Artists
Pop Art emerged as a vibrant and influential artistic movement in the mid-1950s, challenging traditional notions of art and embracing the popular culture of the time. With its bold imagery, vibrant colors, and incorporation of everyday objects, Pop Art brought art closer to the masses. This article explores the definition, key characteristics, notable artists, and lasting impact of Pop Art on the art world and popular culture. What is Pop Art? Pop Art, short for "popular art," was a movement that emerged in the United States and the United Kingdom during the 1950s and 1960s. It was a reaction against the dominant abstract expressionist movement, which focused on subjective, introspective, and non-representational art. Pop Art, on the other hand, celebrated the ordinary, the commercial, and the mundane, drawing inspiration from mass-produced consumer goods, advertising, and popular culture. What are the characteristics of Pop Art? Appropriation and Repetition: Pop Art often incorporated images and objects taken from popular culture, such as product packaging, comic books, and celebrities. Artists manipulated and repeated these images to highlight their significance and challenge the concept of originality. Bold Colors and Simplified Forms: Pop artists used vibrant, eye-catching colors to attract attention and evoke a sense of consumerism. They simplified forms and employed graphic techniques, reminiscent of advertising and comic book aesthetics. Irony and Critique: Pop Art often conveyed a sense of irony and critique by juxtaposing disparate elements, subverting traditional art forms, and challenging societal norms. It questioned the boundaries between high and low culture, art and mass production, and the commercialization of society. Leading Artists of the Pop Art Movement Andy Warhol: One of the most iconic figures associated with Pop Art, Warhol employed screen-printing techniques to reproduce everyday objects, such as Campbell's soup cans and Coca-Cola bottles. His work explored themes of consumerism, fame, and the cult of celebrity. Roy Lichtenstein: Lichtenstein is renowned for his comic book-inspired paintings, featuring bold lines, Ben-Day dots, and speech bubbles. By appropriating and enlarging comic strip panels, he elevated popular culture to the realm of high art. Claes Oldenburg: Oldenburg's sculptures took ordinary objects and transformed them into monumental works of art. His oversized sculptures of hamburgers, typewriters, and clothespins challenged the viewer's perception of scale and materiality. Richard Hamilton: Considered the father of British Pop Art, Hamilton explored the relationship between art and technology. His collage-like works incorporated images from advertising, cinema, and popular magazines, reflecting the media-saturated society. Impact and Legacy Pop Art's influence extends far beyond its initial emergence in the 1960s. Its vibrant and accessible style has had a lasting impact on contemporary art, design, fashion, and popular culture. Pop Art paved the way for subsequent art movements such as Neo-Pop, Street Art, and the appropriation art of the 1980s. It blurred the boundaries between high and low art, challenged the traditional notions of artistic value, and emphasized the democratization of art. Concluding Remarks Pop Art revolutionized the art world by breaking away from the abstract and introspective tendencies of the time. It celebrated the everyday, the commercial, and the popular culture, making art more accessible to a wider audience. Through its use of appropriation, bold colors, and irony, Pop Art continues to captivate and inspire, leaving an indelible mark on contemporary art and popular culture.

ART 101
Exploring Art Medium: A Fusion of Category and Material in Art Creation
Art is a vast and diverse realm that encompasses a wide range of creative expressions. Within this realm, the concept of "Art Medium" holds a crucial role, serving as the bridge between artistic intent and tangible creation. The medium that an artist chooses to work with can have a significant impact on the style and meaning of the artwork. For example, a painting made with oil paints will have a different look and feel than a painting made with watercolors. In the context of Art attribution "Art Medium" has been used interchangeably to refer both the category of artwork and the materials used to bring forth an artist's vision. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of art medium, exploring its dual significance in the world of art. Art Medium as a Category of Art In its first sense, an art medium represents the various categories or disciplines within the field of art. Each medium possesses distinct characteristics, techniques, and artistic approaches. Let's explore some of the prominent art mediums: Painting: Painting is a traditional and widely recognized medium that employs pigments on surfaces such as canvas, paper, or wood. It encompasses various styles like oil painting, watercolor, acrylics, and mixed media, each offering unique visual qualities and expressive possibilities. Painting, Pop Horizon by Barron Holand Sculpture: Sculpture involves shaping and manipulating materials such as stone, wood, metal, clay, or even found objects. Artists create three-dimensional forms that can range from classical figurative representations to abstract and conceptual installations. Sculpture, S-04 BIG FOOT by Aleks Rosenberg Drawing: Drawing is a fundamental art medium that employs pencils, pens, charcoal, or other tools to create two-dimensional representations. It encompasses techniques like sketching, shading, and hatching, allowing artists to convey ideas, explore compositions, and develop their artistic skills. Drawing, Dancer in Red by NK Hong Photography: Photography born from the marriage of science and art, captures moments through the lens of a camera. It employs light-sensitive materials and digital technologies to immortalize scenes, people, and emotions, providing a unique perspective on the world. Photography, La grève Je T'aime by Gudzovsky Printmaking: Printmaking encompasses various techniques such as etching, lithography, screen printing, and relief printing. Artists create multiple copies of their artworks, each possessing its own subtle variations, by transferring images onto paper or other surfaces. Ceramics: Ceramics involves working with clay, shaping it into objects, and firing them in kilns to achieve hardness and permanence. This ancient medium encompasses functional pottery, decorative vessels, sculptures, and intricate porcelain works. Textiles: Textile art employs fabrics, threads, and fibers to create tactile and visually engaging works. It includes techniques like weaving, embroidery, quilting, and textile installations, exploring themes of culture, identity, and materiality. Installation and Performance Art:: These mediums go beyond traditional forms, embracing immersive experiences and the participation of the audience. Artists use various materials, space, sound, and movement to create site-specific installations or enact performances that challenge the boundaries of art. Digital NFT: Very recently Digital NFT is being regarded as an art medium, and more importantly revolutionising Digital Art representation. Utilizing blockchain technology, NFTs represent unique digital assets, such as artwork, music, or videos, providing a secure and verifiable link between the digital file and ownership rights. Art Medium as Material Used in Art Creation In the alternate context, an art medium refers to the specific materials and tools employed by artists to bring their artistic visions to life. The choice of medium significantly influences the aesthetic outcome and the creative process itself. Artists often use it to describe how they created their artwork, which gives a sense of how it needs to be viewed as well. For e.g. Oil paintings ( referenced as "Oil on Canvas") are best observed from a distance to get a more clearer understanding and the depth of the Art. Again depending on the Category of work there are different materials used to fulfill the Artistic vision of the creator. Here are some examples of art mediums in the context of Material Used Paints: Artists use various types of paints, including oil paints, watercolors, acrylics, and gouache, each with its own characteristics and techniques. These pigments, when combined with binders, allow artists to manipulate color, texture, and opacity on different surfaces. A combination of the paint type and the support used form the Medium used for the artwork, for e.g. Oil on Canvas, Gouache on paper, Acrylic on Linen etc... Drawing Tools: Pencils, pens, charcoal, markers, and pastels are all examples of drawing tools that artists employ. These tools vary in hardness, texture, and line quality, enabling artists to create intricate details or bold, expressive strokes. Sculpting Materials: Sculptors utilize a plethora of materials such as stone, wood, metal, clay, plastic, and even unconventional materials like ice or food. Each material offers its unique qualities, texture, and potential for manipulation. Cameras and Photographic Equipment: With the advent of photography, cameras and photographic equipment became vital art mediums. Film cameras, digital cameras, lenses, lighting equipment, and photo-editing software all contribute to the creation of photographic art. Printmaking Supplies: Printmaking relies on materials like printing plates, inks, brayers, and printing presses. These tools facilitate the transfer of images from the plate to the chosen substrate, resulting in distinct prints with their own visual characteristics. Clay and Kilns: Ceramics artists employ different types of clay, glazes, and firing techniques to shape and fire their creations. The firing process in kilns transforms the raw materials into durable and visually captivating ceramic pieces. Fabrics and Threads: Textile artists utilize a wide range of fabrics, threads, dyes, and surface design techniques to create intricate tapestries, clothing, quilts, or fiber-based sculptures. The choice of fabric and the application of techniques contribute to the overall visual and tactile impact of the artwork. The Importance of Art Medium The medium that an artist chooses to work with can have a significant impact on the style and meaning of the artwork. For example, a painting made with oil paints will have a different look and feel than a painting made with watercolors. The medium can also affect the way that the viewer interacts with the artwork, an example being, a sculpture that is made from metal will feel different to the touch than a sculpture that is made from wood. The art medium is of utmost importance in the representation of art as it influences the aesthetics, technical possibilities, symbolic significance, and cultural context of an artwork. It allows artists to express their vision, engage viewers, and communicate their intended messages effectively. The careful consideration and deliberate selection of the art medium contribute to the overall artistic expression and impact of the artwork.Different art mediums have evolved throughout history and across cultures, reflecting the societal and historical context in which they originated. The selection of a particular medium can evoke associations and references to specific art movements, traditions, or periods. The Future of Art Mediums The art world is constantly evolving, and new art mediums are being developed all the time. For example, digital art is becoming increasingly popular, as artists use computers and other digital tools to create their work. It is impossible to predict what the future holds for art mediums. However, it is likely that new art mediums will continue to be developed, and that artists will continue to experiment with different materials and techniques. It's important to note that the future of art mediums will be shaped by the creativity and experimentation of artists themselves, as they continue to push boundaries, embrace new technologies, and explore innovative approaches to art-making. The possibilities are vast, and the future of art mediums for visual artists holds exciting potential for artistic expression and engagement with audiences. Digital, Augmented and Virtual Realities, Mixed Media, Eco-Friendly Materials, BioArt and Living Materials, all are being explored, included and evolved for Artists to continously push the boundaries of their creative abilities to produce thought provoking artworks. Conclusion In the realm of art, the term "art medium" embraces a dual meaning. It encompasses both the categorization of art forms and the materials employed by artists. The category of art medium reflects the different disciplines and techniques artists employ to create their work, while the material aspect highlights the tangible tools and substances used to manifest their creative visions. Artists' choices of medium significantly influence the visual, tactile, and conceptual qualities of their artworks. Furthermore, contemporary artists often push the boundaries of traditional mediums by exploring hybrid forms and incorporating new technologies. Understanding the significance of art medium enhances our appreciation for the diverse expressions and the innovative approaches artists employ in their creative endeavors.








