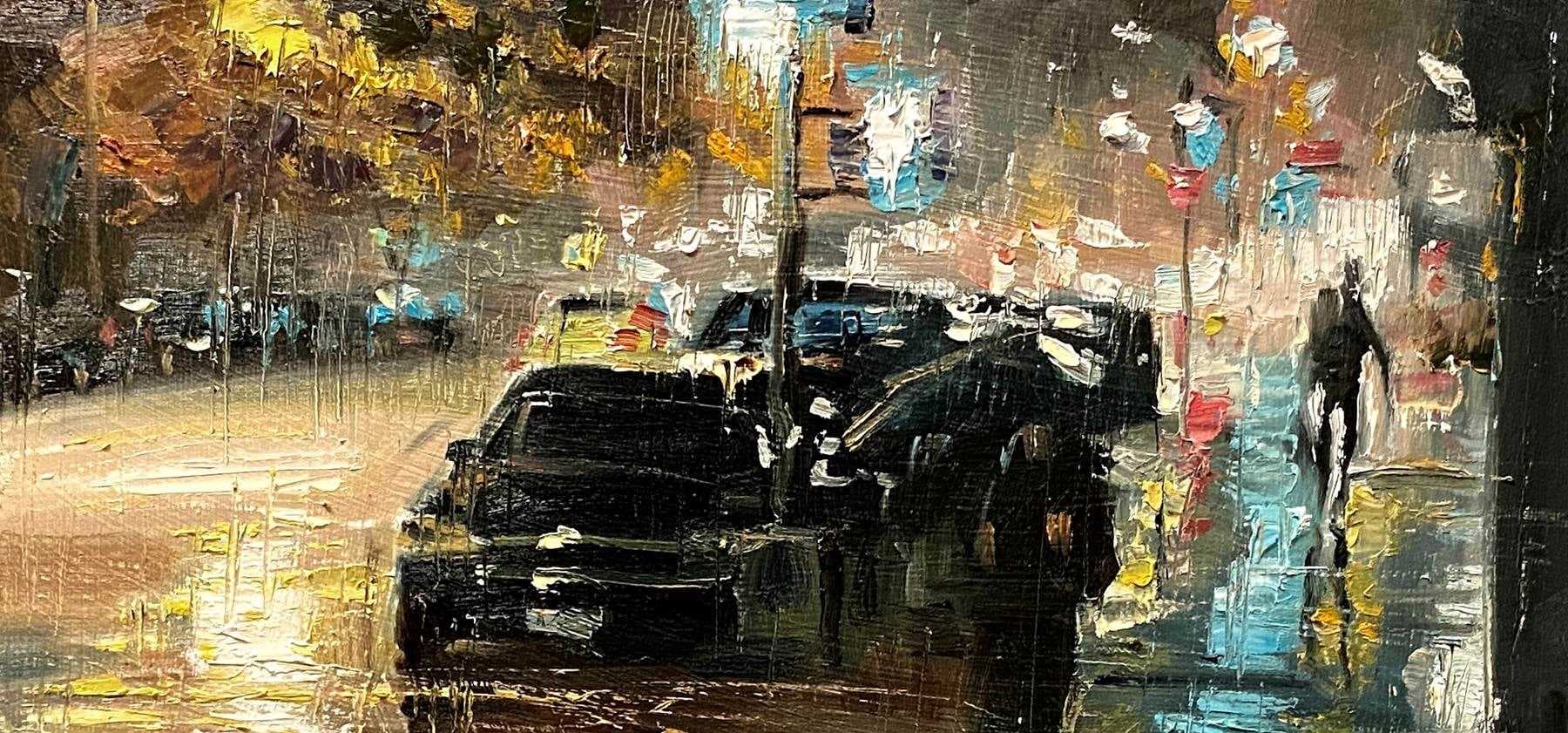Subscribe for our newsletter to have the latest stories and curated art recommendations delivered straight to your inbox
Understanding the Distinction: Contemporary Art vs Modern Art
RTISTIQ TEAM
 Like
Like comments
comments SAVE
SAVEOver several centuries, Art has evolved with various movements and styles shaping its rich history. Two terms that often confuse people are "contemporary art" and "modern art", more in the context that the words Contemporary and Modern are used interchangeably to mean something in-trend now. While these terms may seem interchangeable, they refer to distinct periods and artistic approaches in the world of art. This article will explore the distinction between contemporary and modern art, shedding light on their characteristics, influences, and significance.
Modern Art
A Historical Breakthrough Modern Art refers to the period of art that emerged in the late 19th century and prevailed until the mid-20th century. It departed from traditional artistic conventions and embraced innovative techniques, materials, and subject matters. Modern artists sought to challenge established norms and explore new ways of representing the world.
One crucial characteristic of Modern Art is its emphasis on experimentation and formal innovation. Artists like Pablo Picasso, Wassily Kandinsky, and Henri Matisse revolutionized art through abstract forms, vibrant colours, and the deconstruction of perspective. They rejected the idea of art solely imitating reality and instead focused on conveying emotional and psychological states.
Moreover, modern art was influenced by historical events and societal changes. The impact of World War I, industrialization, and rapid urbanization fueled the desire for artistic expressions that reflected the tumultuous times. Movements such as Cubism, Fauvism, and Surrealism emerged, each with its unique style and thematic focus.
Contemporary Art
Reflections of the Present In contrast, contemporary art encompasses the artistic practices and expressions of the present time. It emerged in the mid-20th century and continues to evolve as new ideas and technologies emerge. Unlike modern art, Contemporary Art does not adhere to a specific style or movement but embraces diversity and individuality.
One defining feature of contemporary art is its inclusivity and openness to various mediums, such as installation, video art, performance, and digital art. Artists like Ai Weiwei, Yayoi Kusama, and Banksy expand the limits of traditional artistic norms and engage with social, political, and cultural issues. Contemporary Art often challenges the viewer's perception, prompting them to question societal norms and ideologies.
Another significant characteristic of contemporary art is its global nature. With the advent of technology and globalization, artists have greater access to diverse cultural influences and artistic practices. This has led to a rich tapestry of creative expressions that transcend geographical boundaries and reflect our world's interconnectedness.

Conclusion
While contemporary art and modern art share a timeline, they are distinct in their approach, style, and influences. Modern Art, emphasizing experimentation and formal innovation, revolutionized the world of Art during the early 20th century. It responded to its time's social and cultural changes and challenged conventional artistic practices.
On the other hand, Contemporary Art reflects the artistic expressions of the present moment. It embraces diversity, inclusivity, and new mediums and technologies. Contemporary artists explore a wide range of themes, often engaging with societal issues and pushing the boundaries of traditional art forms.
By understanding the differences between Contemporary Art and Modern Art, we can better appreciate the unique contributions of each period and gain a deeper insight into the ever-evolving world of Art.
Cover image via Paul Cheng (United States) - Heavy Rain Street
Explore our Curated Collections
SIMILAR ARTICLES

Understanding Abstract Art
Numerous theoretical ideas deal with abstract art. While some have taken the idea of “art for art’s sake,” others have implied that art should be like music; just as music is patterns of sound, art should be created by pure patterns of form, color, and line; there are those who see abstract art as carrying a moral dimension, abstract art can be seen to stand for virtues such as purity and spirituality; and finally, those using the term “abstract” formally, as a distinction from figuration in art (as in non-figurative). How Abstract Art impacts our mental process Abstract art seems to elicit different mental processes than figurative art. While representational art requires a more local and object-focused scan pattern, abstract art involves more globally distributed viewing patterns. Our brain adopts a more exploratory strategy for seeking visual clues while staring at abstract art. Hence more complex areas of our brain seem to be stimulated by abstract art. Appreciating abstract art To claim to understand abstract art is like pretending to understand the Universe; its complexity is beyond us. When it comes to abstract art, a more appropriate approach would be to learn to appreciate it. We can do this with an open mind and heart by looking for clues in the feelings and ideas it arises in us – the emotional approach. Nevertheless, art in general and abstract art in particular should and must be interpreted in its historical context. Despite claiming to be a universal form of art, the ideas behind abstract art were very much generated by a cumulus of factors converging at certain point in time – rational approach. First Experiments towards abstraction The big revolution in art and the journey towards Abstraction began with the Modernist artistic movements. The pioneering artists of the 19th century (Claude Monet, Paul Cézanne and George Surat among others) had a burning desire to innovate, not only because the Academic Art was not representative for an industrial society but they felt the menace of a new invention called daguerreotype. The growing popularity of the first photo camera was threatening the artists´ role of depicting reality, this is when the modern artists started to reject traditional three-dimensional space and instead used flat areas or patches of colour to create a new pictorial space. The Avant-garde - shapes and colours The following generation of Avant-garde artists proved to be even more radical and searched for inspiration far away from Europe, in the ancestral cultures of the African tribes. The Fauvists (like Henry Matisse or André Derrain) were interested in the scientific colour theories and in the use of complimentary colours for creating tension on the canvas. For many of the artists who adopted a fauvist approach it became a transitional stepping stone for future developments in their style, towards abstraction. The Cubists (George Braque, Pablo Picasso or Juan Griss) proposed a new way of depicting an object: multiple viewing angles layered on the canvas. The fragmentation and reassembling of the world proposed by the Parisian cubists had encouraged several other artists, especially from countries such as Holland and Russia, to push farther into a world of forms, leaving behind any reference to recognizable objects or scenes. The invention of these new kinds of abstract or "non-objective" art coincided with the cataclysm of World War I, and the artists involved explained their innovations in terms of contemporary revolutions in both society and consciousness or as the emergence of a changed human order. Inventing abstraction - Wassily Kandinsky “Colour is the keyboard, the eyes are the harmonies, the soul is the piano with many strings. The artist is the hand that plays, touching one key or another, to cause vibrations in the soul.” - Wassily Kandinsky Until the end of the 19th century, the value of a painting was judged by its ability to represent reality. For this reason, music was often regarded by artists as a pure form of art. One of these artists was the Russian born Wassily Kandinsky. The future inventor of Abstraction was born on December 4, 1866 in Moscow and had a formal training in law, economics and ethnography. However, by the age of 30 he had abandoned a career in law; he had fled his native country for Munich, in order to pursue his passion for art. While still living in Russia, Kandinsky found an important connection between colour and music. He is believed to have had synaesthesia, a condition that makes people perceive colour not only as a visual property of objects, but to associate colours with sounds of different qualities and intensities. He was convinced that painting, alike music, must fulfil a spiritual role. Although Kandinsky had developed the philosophical foundation for an abstract art as early as 1909, he had been hesitant to abandon representation. After hearing Arnold Schoenberg’s concert in January 1911, his work took a completely new turn. In the following days he made quick sketches of that performance and he further diluted these drawings until only traces of the original subject remained in his paintings. Composition V – first abstract painting? In the summer of the same year, Kandisnky began working on Composition V, a monumental painting in size, the most radical painting displayed at that time, announcing his ambitions for abstraction. Just a few months later, after being rejected by the official salon, he included the picture in the first exhibition of Der Blaue Reiter (the Blue Rider), a group co-founded together with Franz Marc (killed during the WWI at 36 years of age). Simultaneously, he published Concerning the Spiritual in Art, one of the first thesis to argue for artistic abstraction. His essay examines the purpose of art and how colours and forms impact the human soul. Since abstract art is freed from representation, colours and forms can display their own spirit and express the feelings of the artists. In his book, Kandinsky declares that the most advanced art offers “emotions that we cannot put into words”. The events of 1911 were equivalent to opening Pandora’s box in art. The invention of a non-objective form of art defined in manifestos as a reflection of the deep transformation in the society, anticipated the devastation of the WWI (1914-1918) but at the same time opened unknown paths for artistic explorations. 1. The Red Tree, 1908-1910, source: Gemeentemuseum den Haag 2. The Grey Tree, 1911, source: Gemeentemuseum den Haag 3. Flowering Apple Tree 1912, source: Tate Modern Piet Mondrian Other artists followed in Kandinsky’s steps on the path of abstraction but no other artist’s body of work can better illustrate the transformation from figurative depiction to abstraction as the Dutch painter Piet Mondrian. Mondrian’s fascination with trees developed out of his earlier landscape painting. After absorbing the influences of Cubism, Mondrian reworked the image of his trees to abstraction, and later on to primary colours. The trunk and branches were transforming into a network of verticals and horizontals. He acknowledged the inspiration of nature but added, “I want to come as close as possible to the truth, and I abstract everything from that until I reach the foundation of things”. No. 5, 1948, Jackson Pollock, sold in 2006 in a private sale for $135 million, according to The New York Times Abstract Expressionism - Abstraction in America “It seems to me that the modern painter cannot express this age, the airplane, the atom bomb, the radio, in the old forms of the Renaissance or of any other past culture. Each age finds its own technique.” Jackson Pollock - interview with William Wright, 1950 Prior to WWII, the art world has been dominated for centuries by Europe but the new geo-political reality was about to reshape dramatically the global art scene. The arrival in the United States of various immigrants associated with the Surrealist movement (André Breton, Max Ernst or Marcel Duchamp) fleeing the war was extremely well timed. The European Surrealist proved to be a great influence on the young artists active in New York at that time. The expanding group of artists including figures such as Jackson Pollock, Mark Rothko, Arshile Gorky, Willem de Kooning, Barnett Newman, Robert Motherwell, Clyfford Still and Adolph Gottlieb was soon labelled as “Abstract Expressionists” despite never being formally organized in an art movement. They were, however, unified to some extent by the patronage of a wealthy heiress, Peggy Guggenheim. She is the first to organize exhibitions for the young artists at her newly open gallery, Art of This Century. No other name could better describe the gallery where Abstract Expressionism would catch the interest equally of art critics and politicians. Jackson Pollock – the star of Abstract Art One of Jackson Pollock’s early works (Guardians of the secret, 1943) demonstrates how stylistic borrowings from the Cubist-derived abstraction, Expressionism and Surrealism were fused with the interest in myth and primitivism and powered by the idea of large scale painting (a symbol of the rebirth of Americana, intensely promoted through the Federal Art Project – part of Roosevelt’s New Deal). Pollock’s experiments didn’t stop at mixing various art influences but he took a very daring approach. His most accomplished works were produced in a dramatically different fashion, he rhythmically dripped and spattered industrial paints, by using a stick instead of a brush, all-over huge expanses of unstretched canvases placed on his studio floor – what became known as “drip painting”. His innovation lies in bringing the process of creation under the spotlights, his Action Painting was almost a mystic parade of gestures. Pollock is hailed by his main promoter, the art critic Clement Greenberg as the inheritor of the European abstract tradition. By the 1949, Pollock acquired appreciable market success so that Life magazine was asking rhetorically in a now famous editorial: “Is he the greatest living painter in the United States?”. The wealthy art-buying class that were Pollock’s enthusiasts incorporated the liberal intellectuals and politicians that were becoming increasingly interested in stepping-up the cold war against Communism. Abstract Expressionism and the Cold War The American administration began a cultural war against the Social-Realism (an art movement associated with the communist regimes) by exporting internationally Abstract Expressionism as a symbol of the western capitalism. Just as the Marshall Plan sought to extend America’s influence in Europe through much needed it economic aid, the touring exhibition organized by MoMA with the support of CIA, sought to gain influence over the hearts of minds of Europe. New York School of Art By the early 1950s, the idea of an art movement called Abstract Expressionism seem more of critics´ invention than a homogenous art movement. Under the umbrella New York School you had on one hand the painters whose work was based on a gestural approach (Gestural Abstraction): De Kooning, Jackson Pollock and Robert Motherwell, on the other hand, artists like Clayford Still, Mark Rothko and Barnett Newman who relied on large fields of colour (Colour Field Painting) to produce solemn effects on their canvases. These artists had an interest in archetype and anima and studied Kandisnky´s theories. Despite their sometimes bombastic spiritual claims and being often criticized for being egocentrics, we should not forget that Newman and Rothko were a response to the history of their times. Human dignity and spiritual aspirations have been completely crushed during the WWII and their art was a way of healing the trauma of this great tragedy of human kind. As Paul Klee remarked in 1915: “The more fearful the world becomes, the more art becomes abstract”. The Legacy Because of the huge influence of Abstract Expressionism in post-war America, other artists and movements are generally understood in relation to it. Ad Reinhardt in the early 1950s and then Frank Stella later in the decade painted abstract canvases, but rejected the Abstract Expressionist based on gesture They instead reinforced the essence of the painting as a physical object through precise geometric forms and smooth application of paint, anticipating the Minimalism art. Since the Abstract Expressionism painting was fundamentally “performative” it is regarded as the starting point for the Happenings (Allan Kaprow) of the 1960. Few decades later Abstract Art fell into semi-obscurity for a while only to be resuscitated and to coexist along a wide variety of art forms and ideas, so typical of our post-modern reality. “Abstraction allows man to see with his mind what he cannot see physically with his eyes… Abstract art enables to perceive beyond the tangible, to extract the infinite out of the finite. It is the emancipation of the mind. It is an exploration into unknown areas.” – Arshile Gorky Author: Floarea Baenziger Refrences: Books: 1. David Hopkins, After Modern Art 1945-2000, Oxford University Press, 2000, pp. 5-33; 2. Robert Hughes, The Shock of the New: Art and the Century of Change, Thames & Hudson Ltd, 2004; 3. Kirk Varnedoe, Pictures of Nothing: Abstract Art since Pollock, Princeton University Press, 2006; 4. Leah Dickerman, Inventing abstraction – How a radical idea changed modern art, 1910-1925, catalogue MoMA, New York, 2013; Articles: 1. Helen A. Harrison, Through a Glass Brightly: Jackson Pollock in His Own Words, The New York Times, Nov. 15, 1998; 2. Pepe Karmel, The Golden Age of Abstraction: Right Now, ARTnews, April 24, 2013; 3. Meyer Schapiro, Nature of Abstract Art, www.on-curating.org, October 2003; 4. Celia Durkin, Eileen Hartnett, Daphna Shohamy, An objective evaluation on the beholder’s response to abstract and figurative art based on construal level theory, PNAS, August 2020. Author: Floarea Bänziger, RtistiQ curator RtistiQ is a leading online art marketplace that features a wide curated selection of Abstract art created by emerging and established artists from all over the world. All artworks are original and blockchain powered so you can shop abstract art with an ease of mind. Discover all abstract artworks here.

Singapore Art and Artists: Exploring the Rich Cultural Tapestry and Creative Expression
Singapore is a vibrant city-state that has a thriving arts and culture scene. Over the years, Singapore has seen the emergence of numerous talented artists who have made significant contributions to the local and international art scene. In recent years, the art scene in Singapore has experienced significant growth and development, further solidifying its position as a vibrant cultural hub. Here's a glimpse into Singapore's art and artists: Art Movements in Singapore: Compared to European and other Asian counterparts, Art is relatively young in Singapore and driven mainly by the many cultures and traditions that make up Singapore society. What makes Singaporean Art more distinct is the merging of Chinese, Malay and European Art forms with a blend of localised cultural heritage, indigenous beliefs and popular practices in Singapore. Here is an overview of the key periods and milestones in the history of visual art in Singapore: Early Art Influences (Pre-19th Century): Before the 19th century, Singapore was primarily a trading port, and the cultures of the Malay Archipelago, China, India, and the West predominantly influenced art. Traditional art forms, such as batik, sculpture, and calligraphy, were practised by local artisans. Colonial Influence (19th-early 20th century): The arrival of British colonial rule in the 19th century brought Western influences to Singapore. European artists and art teachers introduced academic art practices, such as oil painting and portraiture, to local students. Notable artists during this period include Raffles Institution founder Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles and his wife, Sophia Raffles. Nanyang Style and Cultural Identity (mid-20th century): In the 1950s, a significant art movement known as the Nanyang Style emerged in Singapore. Led by four master artists of the time, Liu Kang, Chen Wen Hsi, Georgette Chen and Cheong Soo Pieng, this movement combined Chinese ink painting techniques with Western art styles, creating a distinctive fusion. The Nanyang Style was a form of cultural expression exploring the identity of the Southeast Asian region and its people. Modern Art Society (mid-20th century): In the 1960s, the Modern Art Society was established, advocating for modern art practices and promoting local artists. This period marked a shift towards experimentation and exploring abstract and conceptual art forms. Artists like Lim Yew Kuan and Anthony Poon were instrumental in driving the development of modern art in Singapore. Contemporary Art and Global Recognition (late 20th century-present): In the late 20th century, Singapore's art scene continued to evolve and embrace contemporary art practices. The opening of institutions like the Singapore Art Museum (SAM) in 1996 and the National Gallery Singapore in 2015 provided platforms for local and international contemporary artists. Singapore's participation in international art events, such as the Venice Biennale and the Singapore Biennale, further propelled its global recognition. Most Notable Artists of Singapore Singapore has been home to many prominent Artists continuously gaining International reputations. Here are some of the most notable and significant artists from the city-state of Singapore Georgette Chen (1906-1993) was a Chinese-born Singaporean painter known for her realistic portraits and landscapes. She is considered one of the pioneers of modern art in Singapore and a key figure of the "Nanyang School" of Art. She had spent much of her early life in China, France and New York, before making Singapore her home in the year 1954 to spend later years of her life. GEORGETTE CHEN, BOATS AND SHOPHOUSES , (credit: Sotheby's) Chen Wen Hsi (1906-1991) was a Chinese-born Singaporean painter known for his lyrical landscapes and portraits. Similar to other prominent artists Chen Wen Hsi, had spent a good part of his life in China before making Singapore his permanent home. He along with four other prominent artists founded the Nanyang Style of Painting in the year 1953, creating a watershed moment for the Singapore Art scene. In 1964 he was awarded with the "Public Service Star" award. One of his paintings "Two Gibbons Amidst Vines", addorns the back of every $50 note of Singapore. The gibbons are there not only to beautify the note but they also signify a great artist who contributed his entire whole life to the art world. Cheong Soo Pieng (1917-1983) was another prominent Chinese-born Singaporean painter known for his abstract paintings. He along with Chen Wen Hsi, Georgette Chen and Liu Kang founded the Nanyang style of art, one of the most important movements of Singapore's cultural History. After migrating to Singapore in 1946, he took up Art teaching at the Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts, and began his fervent amalgamation of Western and Chinese pictorial styles. Best known for his stylized depictions of Malay and Balinese women, he worked in a unique aesthetic that blended Hindu, Chinese, and Modernist European influences. Lim Tze Peng (born 1921) is a Singaporean painter known for his Chinese ink paintings. He is considered one of the most influential artists of his generation in Singapore. His masterpieces have been exhibited in many local and international exhibitions and prominent art centers in Singapore, including the Singapore Art Museum and Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts.. Hundred and two years old Mr Lim currently is the oldest living Artist of Singapore and was awarded the Cultural Medallion in 2003 for his vast contributions to the Art and Culture of the Country. LIM TZE PENG (courtesy South China Morning Post) Amanda Heng (born 1951): Amanda Heng is a contemporary artist known for performing art and installations. She often addresses issues of gender, identity, and social norms in her works and has exhibited her art internationally. She rose to pominance in the 1990's and is considered a pioneer of Performance Arts in Singapore. She is among the first Singaporean Artists to win the distinguished Benesse Prize and also awarded Cultural Medallion for Visual Arts in 2010. Among the many firsts that she brought to the Art scene in Singapore, includes the founding of the Artists Village in 1988 and then later in 1999 she formed the Women in The Arts (WITA) Collective, the first Artists run collective in Singapore. Tan Swie Han (born 1943) Born in Indonesia Tan Swie Han is a Singaporean multi-disciplinary Artist who migrated from Indonesia in 1946 and is known for his Chinese calligraphy and Contemporary Art Sculptures. He is also distinguished as being the most expensive artist in Singapore after he sold his painting "Moon is Orbed" for S$3.7M in the year 2012 and later again broke his own record by selling his ink on rice-paper artwork "Bada Shanren" for S$4.4M. Tan Swie Han (courtesy Straits Times) Yeo Shih Yun (born 1976): Yeo Shih Yun is a Singaporean artist known for her abstract ink paintings. She combines traditional Chinese ink painting techniques with contemporary approaches, creating bold and expressive artworks reflecting her experiences and emotions. Jane Lee (born 1963): Jane Lee is a contemporary artist known for her experimental approach to painting. She often uses unconventional materials such as epoxy paint and polyurethane foam to create textured and multi-dimensional artworks that challenge traditional notions of painting. Lee has toyed with the painting structure to create rich and tactile abstract works that frequently combine two into three dimensions. These are just a few examples of the many talented artists from Singapore who have significantly contributed to the local and international art scene. The art scene in Singapore continues to evolve and grow, with new artists constantly emerging and pushing the boundaries of artistic expression. Head on to our curated collection Inspired-By-Singapore with a selection of works created by Artists worldwide that could illustrate different sides of Singapore's cultural diversity. Part of this collection is a selection of paintings by the Australian artist Dean O'Callaghan painted and inspired by Singapore's cityscapes and exclusively available on RtistiQ.

Traditional Indian Art Styles in Modern Age
When one brings up the topic of Unity in Diversity, India comes up in most of the conversations. This is not an anomaly per-se but India has been an example of different diverse cultures, languages, art forms, religions and a lot more existing in peaceful coexistence with each other within the same geographical boundaries. In a number of ways, these diverse elements fuse together to produce even more new hybrid elements. Keeping these cultural forces in mind India has been home to a number of schools and styles of paintings, which have evolved over a period of time since 1000’s of years, maybe even more. In their original forms these paintings were done mostly on flat surfaces like rock shelters, house walls, floors and murals. It was later that these styles were adapted on various other mediums like ceramics and fabrics. Each major school of painting has a unique story to tell and these paintings help art historians re-construct the past cultures. These paintings depict the past lives of the contemporary people who made them like their daily practices, religious rituals, favorite past times, festivals and many more anecdotes. Warli The earliest evidence of art comes in the form of Prehistoric Art, like one sees at the Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka. Warli Art derives its origins from this prehistoric art. It is widely prevalent in rural districts of Thane and Nasik and other small parts of Maharashtra. This is a monochromatic art style in which twigs are used with rice paste. Usually white and yellow color on red mud walls is seen on the walls of houses. These paintings depict the everyday life of the village dwellers like their religious rituals, hunting practices and their festivals. In the 1970's, this ritual art took a radical turn when Jivya Soma Mashe and his son Balu Mashe started to paint. They painted not for ritual purposes, but because of their artistic pursuits. Jivya is known as the modern father of Warli painting. Since the 1970s, Warli painting has moved onto paper and canvas. Courtesy: http://godivinity.org/quiz-time-warli-art/ Madhubani This art form has mythical origins. According to a lot of contemporary village based artists who have kept this tradition alive, this painting style originated under the great King Janak of Mithila, which is present day Bihar and regions of Nepal. Till 1934, the outside world was oblivious about this art form. It was British Officer William G. Archer who saw some illustrations on the walls of houses of Bihar that had broken down in an earthquake. This art form uses simple floral, geometric and Indian Mythical designs and illustrations on colorful, symmetrical backdrops. Even today, Madhubani is a very popular folk art form. There are five schools within this art form which are, Bharni, Katchni, Tantric, Godna and Kohbar, which were primarily done by Upper Caste women in India and Nepal. Nowadays the Art Form has received a global outlook, which has made the Art Form go above the Caste System and there is no difference in the style practiced. Madhubani painting received official recognition in 1969 when Sita Devi (Padma Shri) received the State award by Government of Bihar. Jagdamba Devi (Padma Shri) was the first artist from Mithila to receive a National Award in Mithila paintings. Satya Narayan Lal Karn, his wife Moti Karn, Mahasundari Devi (Padma Shri), Baua Devi, Yamuna Devi, Shanti Devi, Chano Devi, Bindeshwari Devi, Chandrakala Devi, Shashi kala Devi, Leela Devi, Godavari Dutta, and Bharti Dayal are the other Madhubani Artists who were adorned by National Awards for their contributions to the Art form. Courtesy: Wikipedia (Kohbar made by artist Padma Shri Sita Devi) Phad This painting style has questionable origins but a lot of scholars are of the opinion that origins of this school of art has its roots with the coming up of Princely States in present day Rajasthan. One can do an approximate dating as this style is only executed on cloth so an educated guess can be around the early medieval period. In this form one comes across horizontal paintings of the lives of Legendary Heroes, Kings and Princes with their wars and other adventures. The most common colors used in this style are red, yellow and orange. It is interesting to see how multiple stories are narrated on a horizontal scroll. Courtesy: Wikipedia (Pabuji Ki Phad, a Phad painting scroll at National Museum, New Delhi) The Joshi families of Bhilwara, Shahpura in Bhilwara district of Rajasthan are widely known as the traditional artists of this folk art-form for the last two centuries. Presently, Shree Lal Joshi, Nand Kishor Joshi, Pradip Mukherjee, Prakash Joshi , Ghanshyam Joshi and Shanti Lal Joshiare the most noted artists of the phad painting, who are known for their innovations and creativity. Kerala Mural Painting Around the same time as the Phad, deep in southern part of the country in Kerala originated a very distinct type of painting style known for its colorful, vivacious and bold strokes. This art form is dated to around 8 th century A.D. so it can actually be put before the Phad in the chronological timeline. This art form developed as a medium of depicting spiritual and religious themes of Shiva, Shakti, Krishna and Mythology. All natural colors are used while executing this art form also known as panchavarna, most common being Ochre-Red, Yellow-Ochre, Bluish Green, Black and White. Courtesy: Yourstory By finding space for mural art outside the temples, it was the late Mammiyur Krishnan Kutty Nair, doyen of modern mural art in Kerala, who gave a new life to it during the last quarter of the twentieth century. Over the past several centuries, the pigments, glues and brushes for the Kerala mural tradition have been derived from natural sources, but now the newer promoters are utilizing modern pigments and colors for the art form Gond Painting This school of painting derives its name from one of the largest, forest dwelling tribal group called the Gonds. The Gonds are found mostly in present day regions of Madhya Pradesh, Vidarbha and Chhatisgarh. This art form is a very unique and intricate style where the painter uses dots and dashes to complete the painting and the painting is executed in such a way that one feels that it is made of straight lines and colors. Lines are used in such a way that it conveys a sense of movement to the still images. In the historic period the colors were naturally extracted from charcoal, cow dung, seed saps and flowers. The Gonds are known for their close affinity with mother nature and hence their paintings mostly depict natural landscapes, wildlife and parts of their stories passed on from generation to generation in the form of Oral Bardic Traditions. Courtesy: Isha Foundation Today, many talented Gond artists' works including Suresh Kumar Dhurve's can be seen on canvases in art galleries internationally. One of the distinctive elements is the use of signature patterns that are used to infill the larger forms on the canvas. Due to the scarcity of natural colors in the current age, Gond artists have started to use poster colors. This combined with the use of canvas has made modern Gond paintings much more vivid than its traditional counter parts. Kalamkari Painting This is one of the most famous art styles of India and it has made a mark in the international art spheres as well thanks to a lot of patronage from people all around the globe. This art style like Madhubani has a very rich antiquity but in material record it appears for the first time on the temple walls of the Sri Kalahasteshwar Temple in Sri Kalahasti, Andhra Pradesh under the Pallava Rulers. Later this temple was further renovated under the Later Cholas and finally new additions like the Gopuram and the thousand pillared hall were made by the famous Vijayanagara Monarch Sri Krishnadevaraya. It was in Sri Kalahasti under the Vijayanagara Patronage that this art form reached its zenith. This painting style started as a temple wall decoration style where themes of mythology and festivities were depicted. Later this art form was adapted on fabric which gave it a huge international market. There are two variants in this style, namely, Srikalahasti and the Machilipatnam style. The Srikalahasti style of Kalamkari, in which the pen or the “kalam” is used for freehand drawing and filling in the colors, is a complete handwork art. Machilipatnam style of Kalamkari craft involves vegetable-dyed block-painting of a fabric. Miniature Paintings During the 10th and 11th Centuries along with the advent of Persian-ate Rule in the Indian Subcontinent a number of Persian-ate elements were introduced by painters from Central Asia like Turks, Persians and Afghans. They introduced what we now call the Miniature Paintings where illustrations are executed from natural stone based colors on paper based ‘wasli’. This painting style reached its zenith under the Mughals and it is known for the intricacy, brush strokes and symbolism. Interesting this painting has affinity with the European Renaissance art in the form of realism that is shown in these paintings. The most common example of these painting style is use of portraits of Kings and Queens to show their heroism and glamour. There are a lot of regional variations of miniature paintings, most common being Kangra, Dakkhani, Mughal, Bundi etc. Tanjore Paintings This style developed in the 1600’s in the state of Thanjavur under the Nayaka Rulers. This art form borrows extensively from the Dakkhani and Maratha miniature painting styles. The most common feature of this school of painting is the use of silver and gold foil. Most common depictions in this art form are scenes from Indian Mythology, Kingly Portraits and scenes of Festivities. Artists have taken this old form of art and over the years combined it with other styles to create mixed media arts. For example, tanjores are also done on mirrors, glass and canvas. The idea of applying gold foil is unique to this traditional art, so this same style is taken and recreated on different mediums. Patachitra This is a late medieval style of painting that originated in present day Odisha. The name Pattachitra has evolved from the Sanskrit words patta, meaning canvas, and chitra, meaning picture. Pattachitra is thus a painting done on canvas, and is manifested by rich colourful application, creative motifs, and designs, and portrayal of simple themes, mostly mythological in depiction. The patuas or the painters of the patachitras were primarily wandering artists- who would travel from place to place with painted scrolls of various deities. However, in recent times, just as the canvas has taken the shape of papers bought easily from the market many a times, the natural colours are also substituted with easily bought acrylic and fabric paints from the market. Pichwai This form of painting style originated as wall hanging cloth paintings behind the Krishna idols in the Krishna Temples of Nathdwara, Rajasthan. Originally only themes from the Krishna Leela were depicted on cloth but as time went by more secular painting themes were executed on cloth for commercial purposes. These paintings are known for colorful, robust and intricate work with concealed hidden meanings within the symbolism. Kalighat Paintings This painting style finds its origins in the mid – 19 th Century Bengal. It is known as Kalighat because it started in the vicinity of the Kali Temple in Kolkata, where Patuas sat and painted mill-made paper with flowing brushwork using earthy colors like indigo, ochre and red. The major inspiration of these paintings are the scenes from the Mythology and Spiritualism, also known as "Oriental school of Kalighat Painting". Under the influence of British and the art schools promoted by them, the “Occidental school, of Kalighat painting” included pieces that depicted ordinary people engaging in everyday life or captured the changes taking place in Kolkata at the time. These paintings are known for their swift, seamless and free flowing outlines. The late artist Jamini Roy is among some of the most acclaimed painters who have been influenced by the distinctive style. Today, Kalighat paintings appear in museums and galleries across the globe, from the Victoria Memorial Hall in Kolkata to the Naprstek Museum in Prague. Hence, one can see how India is a melting pot where a number of painting styles originated. However, due to Globalization and Industrialization these native folk painting styles are losing their importance and there is a lot of lack of awareness among the current urban middle and affluent class of India, who are mostly exposed to foreign painting and art forms. The Indian Government and a number of NGO’s are trying to spread awareness about these painting styles so that they can be revived. E-Commerce platforms like RtistiQ are trying to take these folk Indian art styles to the International market where these paintings can be sold and hence create a livelihood for the artists and help keep these old traditions alive. Author: Kush Dhebar
ARTICLES ON ART 101

ART 101
Art Deco Styles: An Iconic Fusion of Elegance and Modernity
Art Deco is a prominent design style that emerged in the 1920s and flourished until the outbreak of World War II. Characterized by its luxurious materials, geometric forms, and streamlined aesthetic, Art Deco became a symbol of glamour and sophistication during the interwar period. This design movement impacted various visual arts, architecture, fashion, and interior design aspects. This article will delve into the captivating world of Art Deco styles, exploring its origins, key characteristics, influential artists and architects, and its lasting legacy. Origins and Influences Art Deco drew inspiration from various sources, blending elements from different cultures, historical periods, and artistic movements. The style's name derives from the 1925 Exposition Internationale des Arts Décoratifs et Industriels Modernes held in Paris, where it was first showcased. However, its roots can be traced back to the early 20th century, influenced by the avant-garde art movements of the time, such as Cubism and Fauvism. One of the significant influences on Art Deco was the discovery of King Tutankhamun's tomb in 1922, which sparked a craze for Egyptian motifs and symbolism. This fascination with ancient Egypt led to incorporation of pyramids, sphinxes, hieroglyphics, and other Egyptian-inspired motifs into Art Deco designs. Additionally, the style's streamlined forms and angular geometry were influenced by the emerging field of industrial design and the aesthetic of machines. Key Characteristics Art Deco is characterized by distinct visual features that make it instantly recognizable. Here are some key characteristics of Art Deco styles: Geometric Shapes: Art Deco embraces geometric shapes, such as zigzags, chevrons, triangles, and stepped forms. These shapes are often used to create dynamic, visually striking compositions. Streamlined Silhouettes: Inspired by the sleek lines of modern technology and transportation, Art Deco features streamlined, aerodynamic silhouettes. These can be seen in the period's buildings, furniture, and even fashion designs. Luxurious Materials: Art Deco celebrates luxury and opulence, employing exotic woods, marble, chrome, glass, and precious metals like gold and silver. These lavish materials contribute to the overall sense of elegance associated with the style. Decorative Elements: Art Deco designs often incorporate elaborate decorative elements, such as sunbursts, stylized floral motifs, and geometric patterns. These decorative details add a touch of sophistication to the overall composition. Bold Colors: Art Deco embraces bold, contrasting colour schemes. Vivid hues like royal blue, emerald green, ruby red, and vibrant yellow are frequently used to create a visually striking impact. Sunburst Motifs: The sunburst motif, symbolizing energy and optimism, is a recurring theme in Art Deco designs. It is often represented as a radiating pattern of geometric lines or a stylized sun. Influential Artists and Architects Numerous artists and architects played significant roles in shaping and popularizing Art Deco styles. Here are a few key figures: Tamara de Lempicka: A prominent Art Deco painter, de Lempicka's works epitomize the style's elegance and glamour. Her portraits often featured fashionable, confident women in luxurious settings. Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann: Ruhlmann was a renowned French furniture designer who created exquisite Art Deco pieces. His furniture designs combined luxurious materials with precise craftsmanship and sleek silhouettes. Erté: A Russian-born artist and designer, Erté was renowned for his extravagant fashion illustrations and costume designs. His work showcased the epitome of Art Deco elegance and sophistication. Raymond Hood: An influential architect, Hood's designs include the iconic Rockefeller Center in New York City. He incorporated Art Deco elements into the skyscraper's design, contributing to the style's popularity in the United States. Clarice Cliff: A British ceramic artist, Cliff revolutionized the pottery industry with her bold and colourful Art Deco designs. Her pottery pieces featured geometric patterns and vibrant glazes. Legacy and Modern Interpretations Although the heyday of Art Deco was in the early 20th century, its influence and appeal continue to resonate in modern design. Art Deco elements can be found in contemporary architecture, interior design, and fashion. In architecture, buildings like the Chrysler Building in New York City and the Napier Municipal Theatre in New Zealand exemplify the enduring impact of Art Deco. These structures continue to captivate audiences with their sleek lines, decorative details, and innovative use of materials. In interior design, Art Deco-inspired furniture and decor remain highly sought after. The style's emphasis on luxury and glamour translates well into modern homes, with its sleek lines and geometric patterns adding a touch of sophistication to any space. Art Deco influences can be seen in the designs of many contemporary fashion houses. The use of bold colours, geometric patterns, and luxurious materials harkens back to the elegance and allure of the Art Deco era. Conclusion Art Deco styles represent a fascinating fusion of elegance and modernity. Emerging in the 1920s, this design movement embraced geometric shapes, luxurious materials, and bold colours. Its influence extended to various artistic fields, leaving an indelible mark on architecture, interior design, fashion, and more. With its timeless appeal, Art Deco continues to captivate audiences and inspire contemporary design. The legacy of this iconic style serves as a testament to its enduring popularity and artistic significance.

ART 101
Exploring Pop Art: Definition, Movement, and Notable Artists
Pop Art emerged as a vibrant and influential artistic movement in the mid-1950s, challenging traditional notions of art and embracing the popular culture of the time. With its bold imagery, vibrant colors, and incorporation of everyday objects, Pop Art brought art closer to the masses. This article explores the definition, key characteristics, notable artists, and lasting impact of Pop Art on the art world and popular culture. What is Pop Art? Pop Art, short for "popular art," was a movement that emerged in the United States and the United Kingdom during the 1950s and 1960s. It was a reaction against the dominant abstract expressionist movement, which focused on subjective, introspective, and non-representational art. Pop Art, on the other hand, celebrated the ordinary, the commercial, and the mundane, drawing inspiration from mass-produced consumer goods, advertising, and popular culture. What are the characteristics of Pop Art? Appropriation and Repetition: Pop Art often incorporated images and objects taken from popular culture, such as product packaging, comic books, and celebrities. Artists manipulated and repeated these images to highlight their significance and challenge the concept of originality. Bold Colors and Simplified Forms: Pop artists used vibrant, eye-catching colors to attract attention and evoke a sense of consumerism. They simplified forms and employed graphic techniques, reminiscent of advertising and comic book aesthetics. Irony and Critique: Pop Art often conveyed a sense of irony and critique by juxtaposing disparate elements, subverting traditional art forms, and challenging societal norms. It questioned the boundaries between high and low culture, art and mass production, and the commercialization of society. Leading Artists of the Pop Art Movement Andy Warhol: One of the most iconic figures associated with Pop Art, Warhol employed screen-printing techniques to reproduce everyday objects, such as Campbell's soup cans and Coca-Cola bottles. His work explored themes of consumerism, fame, and the cult of celebrity. Roy Lichtenstein: Lichtenstein is renowned for his comic book-inspired paintings, featuring bold lines, Ben-Day dots, and speech bubbles. By appropriating and enlarging comic strip panels, he elevated popular culture to the realm of high art. Claes Oldenburg: Oldenburg's sculptures took ordinary objects and transformed them into monumental works of art. His oversized sculptures of hamburgers, typewriters, and clothespins challenged the viewer's perception of scale and materiality. Richard Hamilton: Considered the father of British Pop Art, Hamilton explored the relationship between art and technology. His collage-like works incorporated images from advertising, cinema, and popular magazines, reflecting the media-saturated society. Impact and Legacy Pop Art's influence extends far beyond its initial emergence in the 1960s. Its vibrant and accessible style has had a lasting impact on contemporary art, design, fashion, and popular culture. Pop Art paved the way for subsequent art movements such as Neo-Pop, Street Art, and the appropriation art of the 1980s. It blurred the boundaries between high and low art, challenged the traditional notions of artistic value, and emphasized the democratization of art. Concluding Remarks Pop Art revolutionized the art world by breaking away from the abstract and introspective tendencies of the time. It celebrated the everyday, the commercial, and the popular culture, making art more accessible to a wider audience. Through its use of appropriation, bold colors, and irony, Pop Art continues to captivate and inspire, leaving an indelible mark on contemporary art and popular culture.

ART 101
Exploring Art Medium: A Fusion of Category and Material in Art Creation
Art is a vast and diverse realm that encompasses a wide range of creative expressions. Within this realm, the concept of "Art Medium" holds a crucial role, serving as the bridge between artistic intent and tangible creation. The medium that an artist chooses to work with can have a significant impact on the style and meaning of the artwork. For example, a painting made with oil paints will have a different look and feel than a painting made with watercolors. In the context of Art attribution "Art Medium" has been used interchangeably to refer both the category of artwork and the materials used to bring forth an artist's vision. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of art medium, exploring its dual significance in the world of art. Art Medium as a Category of Art In its first sense, an art medium represents the various categories or disciplines within the field of art. Each medium possesses distinct characteristics, techniques, and artistic approaches. Let's explore some of the prominent art mediums: Painting: Painting is a traditional and widely recognized medium that employs pigments on surfaces such as canvas, paper, or wood. It encompasses various styles like oil painting, watercolor, acrylics, and mixed media, each offering unique visual qualities and expressive possibilities. Painting, Pop Horizon by Barron Holand Sculpture: Sculpture involves shaping and manipulating materials such as stone, wood, metal, clay, or even found objects. Artists create three-dimensional forms that can range from classical figurative representations to abstract and conceptual installations. Sculpture, S-04 BIG FOOT by Aleks Rosenberg Drawing: Drawing is a fundamental art medium that employs pencils, pens, charcoal, or other tools to create two-dimensional representations. It encompasses techniques like sketching, shading, and hatching, allowing artists to convey ideas, explore compositions, and develop their artistic skills. Drawing, Dancer in Red by NK Hong Photography: Photography born from the marriage of science and art, captures moments through the lens of a camera. It employs light-sensitive materials and digital technologies to immortalize scenes, people, and emotions, providing a unique perspective on the world. Photography, La grève Je T'aime by Gudzovsky Printmaking: Printmaking encompasses various techniques such as etching, lithography, screen printing, and relief printing. Artists create multiple copies of their artworks, each possessing its own subtle variations, by transferring images onto paper or other surfaces. Ceramics: Ceramics involves working with clay, shaping it into objects, and firing them in kilns to achieve hardness and permanence. This ancient medium encompasses functional pottery, decorative vessels, sculptures, and intricate porcelain works. Textiles: Textile art employs fabrics, threads, and fibers to create tactile and visually engaging works. It includes techniques like weaving, embroidery, quilting, and textile installations, exploring themes of culture, identity, and materiality. Installation and Performance Art:: These mediums go beyond traditional forms, embracing immersive experiences and the participation of the audience. Artists use various materials, space, sound, and movement to create site-specific installations or enact performances that challenge the boundaries of art. Digital NFT: Very recently Digital NFT is being regarded as an art medium, and more importantly revolutionising Digital Art representation. Utilizing blockchain technology, NFTs represent unique digital assets, such as artwork, music, or videos, providing a secure and verifiable link between the digital file and ownership rights. Art Medium as Material Used in Art Creation In the alternate context, an art medium refers to the specific materials and tools employed by artists to bring their artistic visions to life. The choice of medium significantly influences the aesthetic outcome and the creative process itself. Artists often use it to describe how they created their artwork, which gives a sense of how it needs to be viewed as well. For e.g. Oil paintings ( referenced as "Oil on Canvas") are best observed from a distance to get a more clearer understanding and the depth of the Art. Again depending on the Category of work there are different materials used to fulfill the Artistic vision of the creator. Here are some examples of art mediums in the context of Material Used Paints: Artists use various types of paints, including oil paints, watercolors, acrylics, and gouache, each with its own characteristics and techniques. These pigments, when combined with binders, allow artists to manipulate color, texture, and opacity on different surfaces. A combination of the paint type and the support used form the Medium used for the artwork, for e.g. Oil on Canvas, Gouache on paper, Acrylic on Linen etc... Drawing Tools: Pencils, pens, charcoal, markers, and pastels are all examples of drawing tools that artists employ. These tools vary in hardness, texture, and line quality, enabling artists to create intricate details or bold, expressive strokes. Sculpting Materials: Sculptors utilize a plethora of materials such as stone, wood, metal, clay, plastic, and even unconventional materials like ice or food. Each material offers its unique qualities, texture, and potential for manipulation. Cameras and Photographic Equipment: With the advent of photography, cameras and photographic equipment became vital art mediums. Film cameras, digital cameras, lenses, lighting equipment, and photo-editing software all contribute to the creation of photographic art. Printmaking Supplies: Printmaking relies on materials like printing plates, inks, brayers, and printing presses. These tools facilitate the transfer of images from the plate to the chosen substrate, resulting in distinct prints with their own visual characteristics. Clay and Kilns: Ceramics artists employ different types of clay, glazes, and firing techniques to shape and fire their creations. The firing process in kilns transforms the raw materials into durable and visually captivating ceramic pieces. Fabrics and Threads: Textile artists utilize a wide range of fabrics, threads, dyes, and surface design techniques to create intricate tapestries, clothing, quilts, or fiber-based sculptures. The choice of fabric and the application of techniques contribute to the overall visual and tactile impact of the artwork. The Importance of Art Medium The medium that an artist chooses to work with can have a significant impact on the style and meaning of the artwork. For example, a painting made with oil paints will have a different look and feel than a painting made with watercolors. The medium can also affect the way that the viewer interacts with the artwork, an example being, a sculpture that is made from metal will feel different to the touch than a sculpture that is made from wood. The art medium is of utmost importance in the representation of art as it influences the aesthetics, technical possibilities, symbolic significance, and cultural context of an artwork. It allows artists to express their vision, engage viewers, and communicate their intended messages effectively. The careful consideration and deliberate selection of the art medium contribute to the overall artistic expression and impact of the artwork.Different art mediums have evolved throughout history and across cultures, reflecting the societal and historical context in which they originated. The selection of a particular medium can evoke associations and references to specific art movements, traditions, or periods. The Future of Art Mediums The art world is constantly evolving, and new art mediums are being developed all the time. For example, digital art is becoming increasingly popular, as artists use computers and other digital tools to create their work. It is impossible to predict what the future holds for art mediums. However, it is likely that new art mediums will continue to be developed, and that artists will continue to experiment with different materials and techniques. It's important to note that the future of art mediums will be shaped by the creativity and experimentation of artists themselves, as they continue to push boundaries, embrace new technologies, and explore innovative approaches to art-making. The possibilities are vast, and the future of art mediums for visual artists holds exciting potential for artistic expression and engagement with audiences. Digital, Augmented and Virtual Realities, Mixed Media, Eco-Friendly Materials, BioArt and Living Materials, all are being explored, included and evolved for Artists to continously push the boundaries of their creative abilities to produce thought provoking artworks. Conclusion In the realm of art, the term "art medium" embraces a dual meaning. It encompasses both the categorization of art forms and the materials employed by artists. The category of art medium reflects the different disciplines and techniques artists employ to create their work, while the material aspect highlights the tangible tools and substances used to manifest their creative visions. Artists' choices of medium significantly influence the visual, tactile, and conceptual qualities of their artworks. Furthermore, contemporary artists often push the boundaries of traditional mediums by exploring hybrid forms and incorporating new technologies. Understanding the significance of art medium enhances our appreciation for the diverse expressions and the innovative approaches artists employ in their creative endeavors.