Subscribe for our newsletter to have the latest stories and curated art recommendations delivered straight to your inbox
Various Techniques and Mediums used in Painting
RtistiQ
 Like
Like comments
comments SAVE
SAVEFine Arts as a discipline has a very rich, vibrant and global antiquity. The discipline has evolved rapidly with time. Art was and is still used as an expression to communicate with the audience. Like people say, ‘A picture is worth a 1000 words’.
Over the huge time span of development of fine arts in human history a number of factors have affected the way art, painting in particular has evolved with time. Some of the major factors that help an artiste or an art critique understand the art work is the contemporary social, economic, religious, environmental and political conditions under which the artiste worked. It is these conditions that also determined the techniques and the mediums which were used to produce these artworks.
All over the world we have the earliest paintings in the form of Rock-Art which date back to the Pre-Historic times. These paintings were very rudimentary line drawings, though very expressive and informative in a number of ways. This art basically depicted the general everyday practices of the people like dancing, hunting and even rituals and beliefs. Since back then there were less technological means to express themselves these Pre-Historic Hominins drew on the walls of natural rock shelters and they used locally available materials, like in case of India, the most well-known Rock Art site is Bhimbetka. Here, the Hominins used animal blood, ox-hide, ochre from locally available banded-hematite quartzite stones and vegetable dies to color.
If one wants to understand the growth and evolution of different painting styles and mediums one needs to understand the growth of society and culture in tandem. Fine Arts could only grow if the society was sedentary, stable and there was regular accumulation of surplus to give attention to other specialized activities. As the division and specialization of labor started getting more granulated more inventions and innovations came forth in Fine Arts as the artistes were given more time and freedom to do so.
In the current Art circles types of paintings are compartmentalized according to the first producers of those paintings, or the first city/state/kingdom the painting was made or the in general the cultural or religious thoughts that were the reason for the development of art.
But however one must understand that it is not correct to believe that painting styles and techniques originated at one specific region and then were disseminated across the world. The scholarship calls this phenomena ‘Unilineal Cultural Evolution’ which is now highly criticized and the belief is of ‘Multilinear Cultural Evolution’ which propounds that ideas could have originated simultaneously in different silos. For example, what we today all know as the Mughal Miniature Painting Style, it is not a very indigenous style, it has characteristics of Persian Painting Style, local Indian variations like Bundi or Deccani Styles and a lot of European Renaissance Style as well. Hence, painting styles, techniques and mediums have constantly been adapted from other regional styles, techniques and mediums.
Keeping the above developments in mind, today, the artistes have managed to enhance their painting styles on different mediums to express their messages to the outside world. Painters today have managed to find the balance between the originalities of various styles and mediums and their personal innovations.
Tempera
Tempera, a traditional painting medium with a rich history dating back to ancient times, remains a captivating choice for artists seeking a luminous and finely detailed aesthetic. Composed of pigments mixed with a water-soluble binder, such as egg yolk, tempera offers a unique balance between opacity and translucency, resulting in artworks that possess both vibrancy and a delicate subtlety. The meticulous nature of tempera painting necessitates careful layering and hatching techniques, allowing artists to achieve intricate textures and meticulous details. Often applied to wooden panels or canvas, tempera creates a surface that is smooth and matte, enhancing the portrayal of intricate subject matter like religious icons, portraits, and intricate patterns. While tempera's historical prominence has evolved with the advent of modern painting materials, its enduring charm lies in its ability to impart a sense of timeless elegance to contemporary and classical artworks alike.

Tempera Art- Last Supper by Da Vinci

Untitled - VII (2020) by Dhrubajyoti Baral
Oil Painting
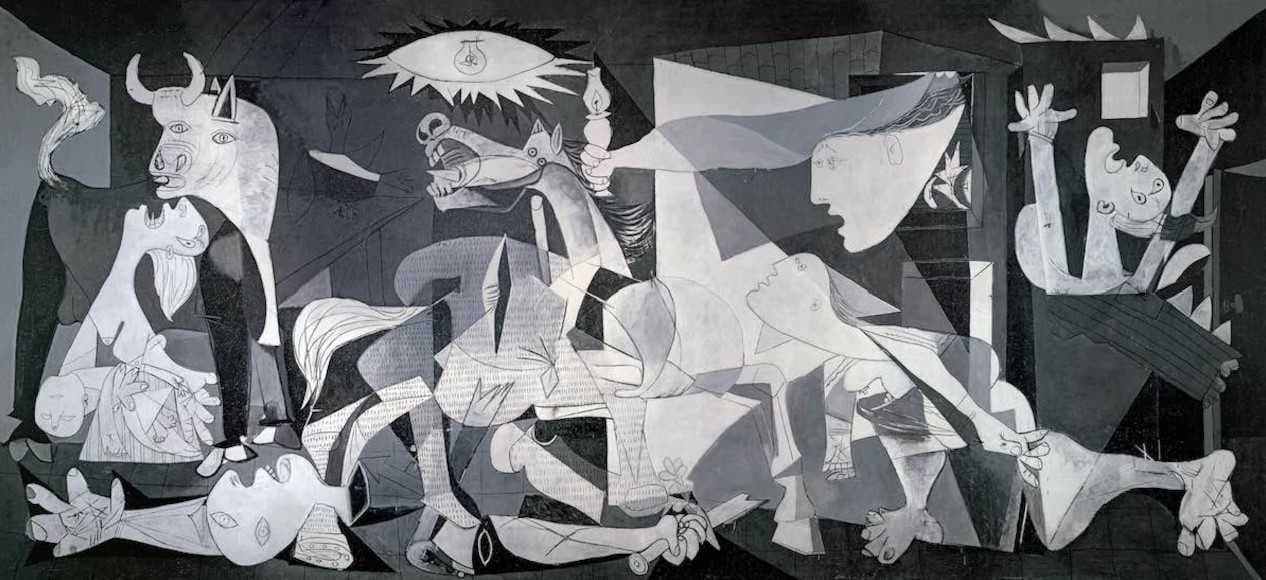
Oil painting, renowned for its depth, richness, and expressive potential, stands as a cornerstone of artistic practice throughout history. This versatile medium involves mixing pigments with linseed oil or other drying oils, creating a paint that dries slowly and allows for extensive manipulation. Oil's hallmark is its capacity to blend smoothly and create subtle gradients, giving artists the ability to capture nuanced transitions of light, shadow, and color. This slow-drying nature grants artists the flexibility to rework and refine their compositions over time, resulting in layered and textured masterpieces that brim with complexity. The luminosity achieved through transparent glazes and the tactile quality of impasto techniques are distinct hallmarks of oil painting. From the opulent portraits of the Renaissance to the evocative landscapes of the Impressionists, oil painting continues to shape the artistic landscape by offering a boundless array of techniques for artists to explore and convey their visions. Painters use different oil paints on the same piece to give it a very distinct multi-dimensional and multi textured look.

Oil Painting- Guernica- Pablo Picasso
Water Colors
Watercolor, celebrated for its transparent and ethereal qualities, captures the essence of lightness and spontaneity in painting. Comprising pigments suspended in a water-based solution, this delicate medium offers artists a unique challenge and reward. Watercolor's fluidity encourages a dynamic interaction between the paint and the surface, resulting in soft washes, subtle gradations, and a luminous effect that allows the white of the paper to shine through. The unforgiving nature of watercolor demands precision and planning, as corrections are limited. This characteristic imparts a sense of immediacy and a fresh, spontaneous quality to artworks. Whether capturing landscapes, florals, or atmospheric scenes, watercolor's ability to evoke emotions through its soft hues and delicate strokes makes it a beloved choice for artists seeking to imbue their creations with a sense of ephemeral beauty and emotional resonance.
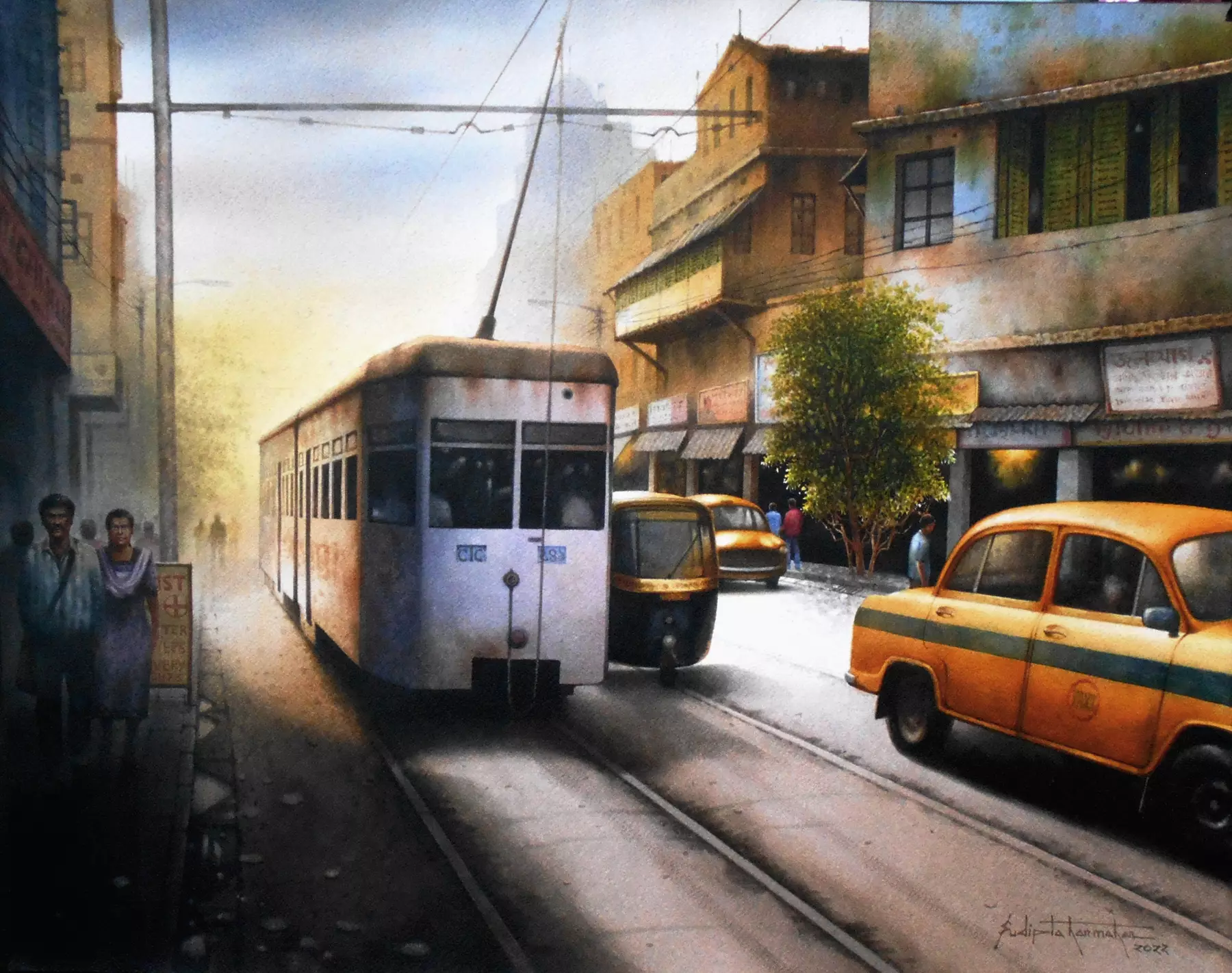
Cityscape (2022) by Sudipta Karmakar
Acrylic Painting
Acrylic painting, a modern and versatile medium, has gained widespread popularity for its quick-drying nature and vibrant results. Comprising pigments suspended in an acrylic polymer emulsion, this medium offers artists a range of possibilities, from bold and energetic brushstrokes to subtle layers of color. Acrylics allow for seamless layering, enabling artists to build up textures, highlights, and shadows with ease. The medium's fast drying time lends itself to experimentation and rapid transformations, as layers can be applied one after another without long waiting periods. Additionally, acrylics can be used on a variety of surfaces, from canvas and paper to wood and even fabric. The ability to mimic the appearance of both watercolors and oils, depending on dilution and technique, makes acrylics a versatile choice suitable for a wide spectrum of styles and subjects. Whether achieving delicate transparencies or vibrant opacities, acrylic painting offers artists a contemporary tool to express their creativity with immediacy and brilliance.
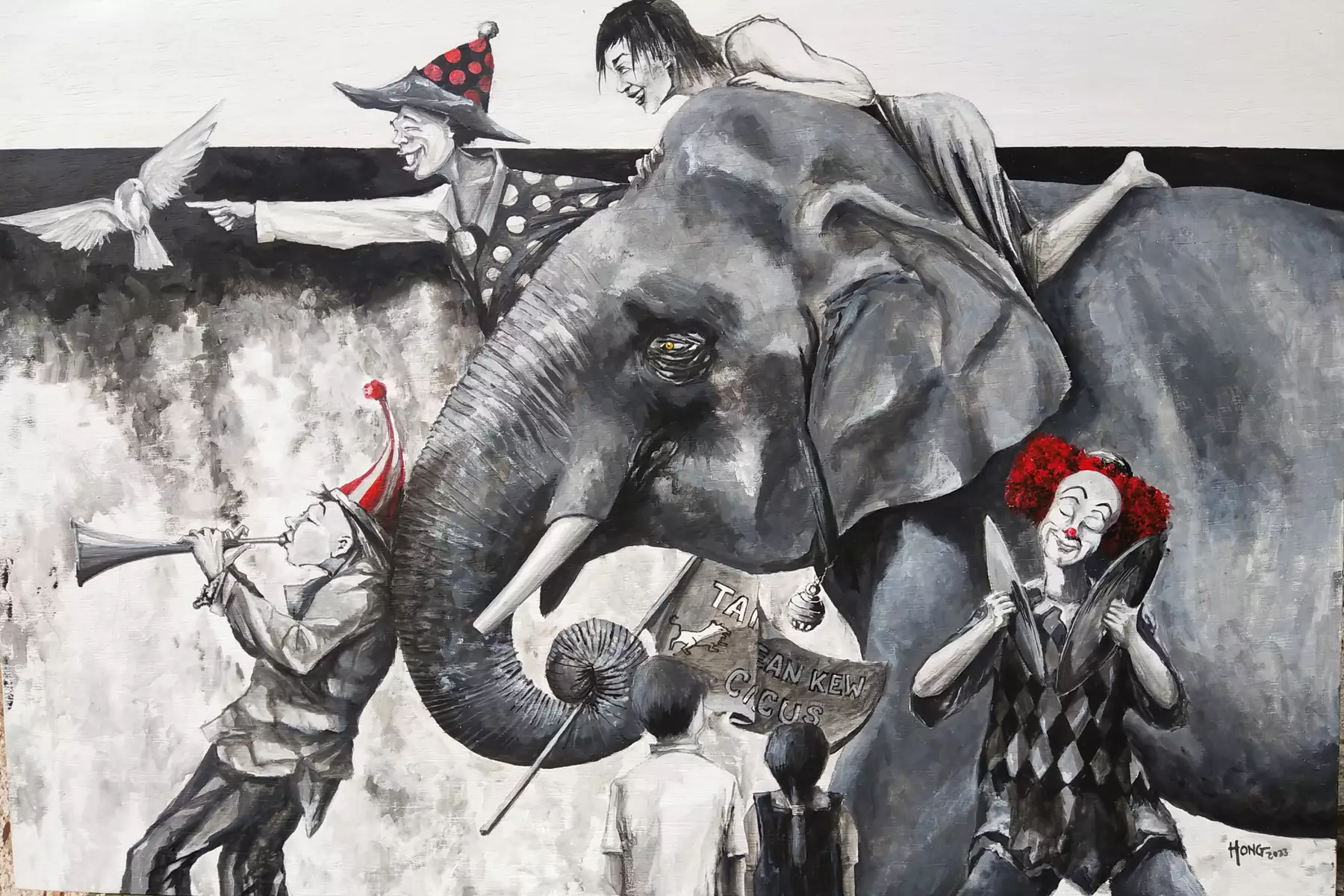

The Circus Parade (2022) by NK Hong
Pen and Ink
Pen and ink, a classic and timeless medium, encapsulates the beauty of intricate detail and expressive line work in visual art. Utilizing a simple combination of pens and ink, artists can create works that range from intricate and delicate drawings to bold and dynamic compositions. The fine control offered by pens enables artists to convey intricate textures, cross-hatching, and stippling with precision, while the contrast between black ink and white paper can evoke a striking visual impact. The versatility of pen and ink is evident as it can be combined with other mediums such as watercolors, creating mixed-media pieces that harmoniously blend the precision of ink with the fluidity of color. From architectural renderings to intricate illustrations, pen and ink's ability to capture both intricate details and sweeping gestures has made it a beloved choice for artists seeking to convey depth and dimension through lines.
This is a truly traditional yet prevalent technique known for its versatility on different mediums. Earliest examples can be found in the form of scrolls from ancient civilizations like at Egypt and China. But predominantly this technique is used today and even in the past for the detailing in the calligraphy or illustrations that it would give. An artiste can focus on the tiniest of details through this technique on mediums like paper, cloth, palm leaves or ceramics. This style is widely used by artistes who work in the illustration business like Graphic Novel or Comic Publishing Houses or Newspapers and Magazines.

Pen and Ink- Mystical European Landscapes- Olivia Kemp
Pastels
Pastels are a captivating and versatile painting medium renowned for their vibrant and luminous qualities. Comprising pure pigment combined with minimal binder, they deliver a direct and intense color application that resonates with a unique visual richness. Pastels exist in various forms, including soft, oil, and hard pastels, each offering distinct textural effects. The velvety texture of soft pastels allows for seamless blending and layering, enabling artists to effortlessly transition between hues and create a smooth gradient of tones. Oil pastels, on the other hand, possess a buttery consistency that encourages both detailed precision and expressive strokes. The remarkable tactile quality of pastels allows artists to capture the essence of their subjects with immediacy, making them a favored choice for portraits, landscapes, and still lifes. Their ability to infuse artworks with an aura of both softness and vibrancy sets pastels apart as a captivating and evocative painting medium.
Several well-known artists have embraced pastels as a medium and have created exceptional artworks that showcase the versatility and beauty of this medium. Some of the more well established artists having known to use pastels as medium include Edgar Degas, Mary Casatt, Odilon Redon, Pierre Auguste Renior and Wolf Kahn. These artists, among others, have contributed significantly to the recognition and appreciation of pastels as a sophisticated and captivating painting medium. Their works demonstrate the wide range of styles and subjects that can be achieved through the skillful use of pastels.

Pastels- Dandelions- Jean Francois Millet
Mixed Media
Mixed media painting is a versatile and creative technique that involves combining various art materials and mediums to create a unified artwork. This approach allows artists to experiment with textures, colors, and techniques that might not be achievable using just one medium. Artists use a combination of paints, ink, chalk, pastels on different mediums like metal, canvas, ceramics and many more. The combined medium has a very individualistic feel, as it gives an artiste the opportunity to experiment in a number of ways.

Mixed Media- Radha Krishna- Revankar Art
Digital Drawings/Paintings
Among the current tech savvy millennial population, the young artistes have started producing phenomenal art using devices and different software. The most common software used are Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator and Adobe InDesign. Through these digital media one can create very detailed and neat illustrations. Secondly, to make sure that a very personal touch is maintained for the artistes there are digital pads like Wacom, on which an artiste can draw using a digital pen and the image appears on the computer screen. At present, this is the most preferred style of drawing and painting used by commercial houses like book publishers or logo designers etc.

Digital Drawing- Game of Thrones- Tommy Patterson
To sum up, Painting Styles and Traditions have long antecedents in our history and they have been evolving with time. One needs to understand the world these techniques emerged in, to fully fathom the symbolic meanings behind them.
Discover more painting styles on RtistiQ, an Online Art Gallery for the Art loving community and creators alike.
Explore our Curated Collections
SIMILAR ARTICLES

History of Oil Paintings
Oil paintings have existed for centuries, from the cave paintings of Bamiyan along the Silk Road to American post-war art. There have been several studies related to the origins of oil as a painting medium with some believing that the technique was first developed in the 11th century, while Giorgio Vasari has credited 15th century Flemish painter Jan van Eyck with the “invention” of oil paints in his famous treatise The Lives of the Artists. However, a discovery in 2008 led to the evidence that oil painting existed as early as 650 CE (7th century CE), when anonymous artists used oil that may have been extracted from walnuts or poppies to decorate the caves in Bamiyan, Afghanistan. The practice of easel painting with oil colours started post-1400 CE, to meet the changing requirements of Renaissance artists who were looking for some other medium than pure egg-yolk tempera. The depth and richness of colour in oil paint is unmatched and it’s slow drying time allows artists to manipulate the medium over an extended period giving the artists the flexibility in blending and layering - thin glazes to dense thick impasto, as well as a wide range of tonal transitions and shades producing both opaque and transparent effects, as well as matt and gloss finishes. Considered a hallmark of the Old Masters, particularly during the Northern Renaissance, oil paint was one of the most preferred mediums for Leonardo da Vinci, Rembrandt, and iconic modernists like Vincent Van Gogh, Pablo Picasso, Wassily Kandinsky and many others. Although there are several remarkable oil paintings by famous artists to study this medium, we have narrowed down the exhaustive list to 10 iconic works. The Arnolfini Portrait by Jan van Eyck Jan van Eyck’s Arnolfini Portrait (1434) remains one of the most visually intriguing paintings of all time. With all of its details and intricacies, the exquisitely rendered work appears to be a straightforward depiction of a wealthy merchant and his wife. However, on a closer look several mysteries emerge along with Van Eyck’s masterful technique which continue to enthrall viewers till today! (Image courtesy: Wikimedia Commons) Mona Lisa by Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa (c. 1503-1519), the painting of a mysterious woman with an enigmatic smile, remains one of the most famous paintings in the world. The sitter is believed to be Lisa Gherardini, the wife of Florence merchant Francesco del Giocondo. The painting is known to be the earliest Italian portrait to focus so closely on the sitter in a half-length portrait. (Image courtesy: Wikimedia Commons) The Rape of Europa by Titian The Rape of Europa (c. 1559-1562), tells the mythological story of the abduction of Europa by the king of gods, Jupiter, disguised as a white bull. An example of Titian’s late style, the painting’s refined poignancy lies in his use of colour, vividity, luminous tints, brushwork and subtlety of tone. The oil painting continues to have a profound influence on Western art. (Image courtesy: Wikimedia Commons) Girl with a Pearl Earring by Johannes Vermeer Sometimes nicknamed the “Mona Lisa of the North”, Girl With a Pearl Earring (1665), is brilliant in its simplicity. The girl, wearing a blue and gold turban and an oversized pearl earring is the entire focus with only a dark backdrop behind her. Interestingly, this masterpiece isn't even a portrait, but a “tronie” - a Dutch word for a painting of an imaginary figure with exaggerated features. (Image courtesy: Wikimedia Commons) Le déjeuner sur l'herbe (or The Luncheon on the Grass) by Édouard Manet Manet's masterpiece, Le Déjeuner sur l'herbe (1863), featuring a nude woman picnicking in the company of fully-clothed men, draws inspiration from classical paintings of female nudes. Up until The Luncheon on the Grass, female nudes were represented figures from mythology or allegory. By placing an anonymous unclothed woman in a contemporary everyday setting, Manet bridged the gap between the Realist and Impressionist art movements with its modern approach to style and subject matter. (Image courtesy: Wikimedia Commons) The Starry Night by Vincent Van Gogh Few artists are as renowned for their use of color as Vincent van Gogh. His The Starry Night (1889) full of striking blues and yellows, and the dreamy, swirling atmosphere have intrigued art lovers for decades. The painting was created late into the Dutch painter's short career and depicts the view from his window in the asylum at Saint-Rémy-de-Provence. (Image courtesy: Van Gogh Gallery) The Old Guitarist by Pablo Picasso Painted at the height of Picasso’s Blue Period, The Old Guitarist (1903) depicts a feeble blind old man hugging his guitar. Picasso painted it after his close friend and Spanish poet Carles Casagemas commited suicide. The melancholic state was used by design to haunt onlookers in a way that would make them question why the working class and high-class individuals continued to prosper while those that needed the most help continued to languish in poverty. (Image courtesy: Wikimedia Commons) The Persistence of Memory by Salvador Dali Salvador Dali’s most iconic work, The Persistence of Memory (1931) was painted at the height of the Surrealist art movement. It displays an outlandish subject matter evocative of a dreamscape, which is why it is believed that Dalí was probably hallucinating when he painted the piece. Dalí would attempt to enter a state of self-induced psychotic hallucinations to create what he called “hand-painted dream photographs.” (Image courtesy: Museum of Modern Art, New York) The Kiss by Gustav Klimt Austrian Symbolist painter Gustav Klimt was famous for his dazzling use of gold to give a shimmering effect to his paintings and his masterpiece The Kiss (1907-1908) is no different. Made in the Vienna Secession art movement, this intimate portrait captures a tender moment between a pair of lovers. (Image courtesy: Google Art Project) Nighthawks by Edward Hopper The highly evocative American masterpiece Nighthawks (1942) is a stark depiction of loneliness, alienation and the breakdown of city life, epitomizing somber emotions of a period in history riddled with world wars and the great depression. The oil painting is said to have influenced the look and feel of many Hollywood films including Ridley Scott’s futuristic neo-noir Blade Runner (1982). (Image courtesy: Wikimedia Commons) Oil paintings are one of the best investments you can make for your home or business. Discover oil paintings for sale on RtistiQ, A Virtual Art Marketplace For Art Lovers And Artists.

Exploring the Intricate Techniques of Islamic Art
Islamic art is a rich and diverse artistic expression shaped by centuries of cultural and religious influences. From calligraphy to geometric patterns, this guide explores Islamic art's various styles and techniques and how they have evolved over time. What are Islamic Art styles and techniques in the contemporary art market? Islamic Art encompasses various styles and techniques, some of which have been adapted and incorporated into contemporary art markets. Here are some examples: Calligraphy: Islamic calligraphy is one of the most recognisable art forms in the world. It involves the writing of Quranic verses or other Islamic phrases in a decorative way. Contemporary artists have experimented with this style by incorporating it into paintings, sculptures, and installations. Calligraphy is also used to decorate buildings, textiles, and other objects, and is often combined with other forms of Islamic art, such as geometric patterns and floral motifs. The beauty of calligraphy lies in its ability to convey meaning and emotion through the careful arrangement of letters and words. Geometric patterns: Geometric patterns are common in Islamic Art and are often used to decorate mosques and other religious buildings. Contemporary artists have also incorporated these patterns into their work, creating modern pieces rooted in Islamic tradition. Some common geometric shapes used in Islamic art include circles, squares, triangles, and stars. These shapes are often combined to create intricate and mesmerizing patterns that are both beautiful and meaningful. Miniature painting: Miniature painting is a traditional Islamic art form that involves creating small, detailed paintings on paper or other surfaces. Contemporary artists have continued to use this technique, often with a modern twist, creating works that are both intricate and innovative. Metalwork: Islamic metalwork is known for its intricate designs and detailed craftsmanship. Contemporary artists have continued to use metalworking techniques to create modern pieces that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Ceramics: Islamic ceramics are often decorated with intricate patterns and designs. Contemporary artists have continued to use this technique, creating modern ceramics that are both beautiful and functional. Islamic art styles and techniques have a rich history that inspires contemporary artists worldwide. By blending traditional Islamic techniques with modern styles and materials, these artists are creating a new and exciting form of Art that celebrates both the past and present. The influence of nature and floral motifs Nature and floral motifs are also commonly found in Islamic art. These motifs are often used to symbolize growth, renewal, and the beauty of the natural world. Islamic artists often use stylized versions of flowers, leaves, and vines in their designs, incorporating them into geometric patterns or using them as standalone elements. The use of nature and floral motifs in Islamic art reflects the importance of nature in Islamic culture and the belief in the interconnectedness of all living things. Working across various disciplines, Mobeen Akhtar details her fondness for arabesque by using natural pigments extracted from minerals, rocks and earth as she aims to practise the traditional methods so they may be recognised and enjoyed today, as they were in the past. The role of color and symmetry in Islamic art Color and symmetry are two important elements in Islamic art. The use of vibrant colors, such as blues, greens, and reds, is common in Islamic art and is often used to create a sense of harmony and balance. Symmetry is also a key feature of Islamic art, with many designs featuring intricate geometric patterns that are perfectly balanced on both sides. This symmetry is believed to reflect the order and balance found in the natural world and is a reflection of the Islamic belief in the unity and harmony of all things. Is Islamic Art a religious-only Art? Islamic Art is not solely religious but strongly connects to the Islamic faith and culture. Islamic Art encompasses various artistic forms and styles, including calligraphy, geometric patterns, miniatures, textiles, ceramics, metalwork, and architecture. Multiple cultures and regions have influenced these art forms throughout Islamic history and have been used for religious and secular purposes. Islamic Art can be found in various settings, from religious spaces like mosques and madrasas to secular areas like homes, palaces, and public buildings. In addition, Islamic Art has been appreciated and collected by people of various faiths and cultures throughout history. While Islamic Art often incorporates Islamic themes and motifs, it is not limited to religious subjects. Many Islamic artists throughout history have drawn inspiration from the natural world, human figures, and other non-religious subjects. In contemporary Art, Islamic art styles and techniques continue to inspire artists of all backgrounds and beliefs. By blending traditional Islamic techniques with modern styles and materials, these artists are creating a new and exciting form of Art that celebrates both the past and present. Is Islamic Art only practised by Muslims? Islamic Art has its roots in the Islamic faith and culture, but it is not limited to only Muslims. Islamic Art encompasses various artistic forms and styles, including calligraphy, geometric patterns, miniatures, textiles, ceramics, metalwork, and architecture. Multiple cultures and regions have influenced these art forms throughout Islamic history, and they have been appreciated and practised by people of different faiths and backgrounds. Many non-Muslim artists and artisans have contributed to the development of Islamic Art throughout history. In medieval Spain, for instance, Christian and Jewish artists worked alongside Muslim artisans to create some of the most stunning examples of Islamic Art and architecture. And in modern times, many contemporary artists and designers from diverse backgrounds have been inspired by Islamic Art and its techniques, incorporating them into their works. Furthermore, many Islamic art forms have been used for religious and secular purposes. Islamic architecture, for example, is often used for public buildings and private homes, regardless of the faith or background of the owner. Similarly, Islamic calligraphy and geometric patterns are often used in various artistic and decorative contexts, from book design to interior decoration. Final Thoughts! In conclusion, Islamic art is a form of art that is enjoyed by people of all backgrounds, cultures, and faiths. Its beauty and significance can be appreciated by anyone with an appreciation for art and culture. Head on to a very special collection of Islamic Art from Artists across different part of the world on RtistiQ - Cultural festivity Art Collection

How to Tell a Lithograph from a Painting: A Comprehensive Guide
Art enthusiasts and collectors often come across various forms of visual art, including lithographs and paintings. While both mediums have their own unique appeal, it is important to understand the differences between them. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to differentiate between a lithograph and a painting, considering their techniques, materials, and characteristics. By gaining insights into these key factors, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to identify and appreciate these art forms more effectively. Understanding Lithographs A lithograph is a type of printmaking technique that involves the process of drawing or painting on a stone or metal plate. It is based on the principle of oil and water repelling each other. The artist creates an image on the stone using specialized tools, and then applies ink to the stone's surface. The ink adheres to the image while being repelled by the wet areas, and a piece of paper is pressed onto the plate to transfer the image. A more detailed article on Lithographs can be referenced in the article What Is A Lithograph. Analyzing Painting Techniques Painting, on the other hand, involves the application of pigments onto a surface, typically canvas, using various tools like brushes, knives, or even fingers. Paintings can be created with different types of paints, such as oil, acrylic, watercolor, or gouache. Artists have greater freedom to manipulate the paint, creating textures, layering colors, and incorporating various brushstrokes, thereby resulting in a unique and original piece of artwork. There are a few key differences between lithographs and paintings that can help you tell them apart. Paper: Lithographs are typically printed on high-quality paper, such as rag paper or watercolor paper. Paintings, on the other hand, can be painted on any type of paper, including newsprint, canvas, or wood. Ink: Lithographs are printed with ink that is specifically designed for lithography. This ink is water-based and has a high viscosity, which means that it is thick and does not flow easily. Paintings, on the other hand, can be painted with any type of paint, including oil paint, acrylic paint, or watercolor paint. Printing process: Lithographs are printed using a process called intaglio printing. This process involves pressing the plate against the paper in a very controlled manner. Paintings, on the other hand, are painted by hand, and there is no such control over the application of paint. Texture: Lithographs typically have a smooth, even texture. Paintings, on the other hand, can have a variety of textures, depending on the type of paint and brushstrokes used. Signature: Lithographs are typically signed by the artist. Paintings, on the other hand, are not always signed. Examining the Surface One of the key ways to differentiate between a lithograph and a painting is by examining the surface closely. Lithographs typically have a flat, smooth texture with even ink distribution. Due to the nature of the printing process, the lines and colors in lithographs tend to be more uniform and consistent. In contrast, paintings often exhibit varied textures, visible brushstrokes, and an overall three-dimensional quality. The presence of texture is a strong indicator of an original painting. Inspecting the Signature Another important aspect to consider is the presence of an artist's signature. In most cases, lithographs are signed in pencil, usually at the bottom margin, while paintings are typically signed in paint directly on the artwork itself. Examining the signature can provide valuable insights into the authenticity and origin of the piece. Additionally, lithographs may have edition numbers or impressions indicating the total number of prints made from the original plate. Assessing the Color Saturation Color saturation is another distinguishing factor between lithographs and paintings. Lithographs tend to have more consistent color saturation throughout the print, with an absence of subtle variations that are commonly seen in paintings. Paintings, on the other hand, often exhibit subtle color shifts, gradients, and nuanced tonal variations, showcasing the artist's hand in mixing and applying the pigments. Considering the Frame and Glass The framing and glass used can also provide clues about whether you're looking at a lithograph or a painting. Paintings are usually framed with a mat and glass, which helps protect the artwork and enhance its presentation. In contrast, lithographs are typically framed without glass, as the glass can cause unwanted reflections and interfere with viewing the image. Moreover, lithographs are often mounted directly on the backing board to prevent any damage caused by the pressure of the glass. Conclusion Distinguishing between a lithograph and a painting requires a keen eye and understanding of the key differences in technique, materials, and characteristics. By examining the surface, signature, color saturation, and framing, you can confidently identify whether you are looking at a painting or a Lithograph.
ARTICLES ON ART 101

ART 101
Art Deco Styles: An Iconic Fusion of Elegance and Modernity
Art Deco is a prominent design style that emerged in the 1920s and flourished until the outbreak of World War II. Characterized by its luxurious materials, geometric forms, and streamlined aesthetic, Art Deco became a symbol of glamour and sophistication during the interwar period. This design movement impacted various visual arts, architecture, fashion, and interior design aspects. This article will delve into the captivating world of Art Deco styles, exploring its origins, key characteristics, influential artists and architects, and its lasting legacy. Origins and Influences Art Deco drew inspiration from various sources, blending elements from different cultures, historical periods, and artistic movements. The style's name derives from the 1925 Exposition Internationale des Arts Décoratifs et Industriels Modernes held in Paris, where it was first showcased. However, its roots can be traced back to the early 20th century, influenced by the avant-garde art movements of the time, such as Cubism and Fauvism. One of the significant influences on Art Deco was the discovery of King Tutankhamun's tomb in 1922, which sparked a craze for Egyptian motifs and symbolism. This fascination with ancient Egypt led to incorporation of pyramids, sphinxes, hieroglyphics, and other Egyptian-inspired motifs into Art Deco designs. Additionally, the style's streamlined forms and angular geometry were influenced by the emerging field of industrial design and the aesthetic of machines. Key Characteristics Art Deco is characterized by distinct visual features that make it instantly recognizable. Here are some key characteristics of Art Deco styles: Geometric Shapes: Art Deco embraces geometric shapes, such as zigzags, chevrons, triangles, and stepped forms. These shapes are often used to create dynamic, visually striking compositions. Streamlined Silhouettes: Inspired by the sleek lines of modern technology and transportation, Art Deco features streamlined, aerodynamic silhouettes. These can be seen in the period's buildings, furniture, and even fashion designs. Luxurious Materials: Art Deco celebrates luxury and opulence, employing exotic woods, marble, chrome, glass, and precious metals like gold and silver. These lavish materials contribute to the overall sense of elegance associated with the style. Decorative Elements: Art Deco designs often incorporate elaborate decorative elements, such as sunbursts, stylized floral motifs, and geometric patterns. These decorative details add a touch of sophistication to the overall composition. Bold Colors: Art Deco embraces bold, contrasting colour schemes. Vivid hues like royal blue, emerald green, ruby red, and vibrant yellow are frequently used to create a visually striking impact. Sunburst Motifs: The sunburst motif, symbolizing energy and optimism, is a recurring theme in Art Deco designs. It is often represented as a radiating pattern of geometric lines or a stylized sun. Influential Artists and Architects Numerous artists and architects played significant roles in shaping and popularizing Art Deco styles. Here are a few key figures: Tamara de Lempicka: A prominent Art Deco painter, de Lempicka's works epitomize the style's elegance and glamour. Her portraits often featured fashionable, confident women in luxurious settings. Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann: Ruhlmann was a renowned French furniture designer who created exquisite Art Deco pieces. His furniture designs combined luxurious materials with precise craftsmanship and sleek silhouettes. Erté: A Russian-born artist and designer, Erté was renowned for his extravagant fashion illustrations and costume designs. His work showcased the epitome of Art Deco elegance and sophistication. Raymond Hood: An influential architect, Hood's designs include the iconic Rockefeller Center in New York City. He incorporated Art Deco elements into the skyscraper's design, contributing to the style's popularity in the United States. Clarice Cliff: A British ceramic artist, Cliff revolutionized the pottery industry with her bold and colourful Art Deco designs. Her pottery pieces featured geometric patterns and vibrant glazes. Legacy and Modern Interpretations Although the heyday of Art Deco was in the early 20th century, its influence and appeal continue to resonate in modern design. Art Deco elements can be found in contemporary architecture, interior design, and fashion. In architecture, buildings like the Chrysler Building in New York City and the Napier Municipal Theatre in New Zealand exemplify the enduring impact of Art Deco. These structures continue to captivate audiences with their sleek lines, decorative details, and innovative use of materials. In interior design, Art Deco-inspired furniture and decor remain highly sought after. The style's emphasis on luxury and glamour translates well into modern homes, with its sleek lines and geometric patterns adding a touch of sophistication to any space. Art Deco influences can be seen in the designs of many contemporary fashion houses. The use of bold colours, geometric patterns, and luxurious materials harkens back to the elegance and allure of the Art Deco era. Conclusion Art Deco styles represent a fascinating fusion of elegance and modernity. Emerging in the 1920s, this design movement embraced geometric shapes, luxurious materials, and bold colours. Its influence extended to various artistic fields, leaving an indelible mark on architecture, interior design, fashion, and more. With its timeless appeal, Art Deco continues to captivate audiences and inspire contemporary design. The legacy of this iconic style serves as a testament to its enduring popularity and artistic significance.

ART 101
Exploring Pop Art: Definition, Movement, and Notable Artists
Pop Art emerged as a vibrant and influential artistic movement in the mid-1950s, challenging traditional notions of art and embracing the popular culture of the time. With its bold imagery, vibrant colors, and incorporation of everyday objects, Pop Art brought art closer to the masses. This article explores the definition, key characteristics, notable artists, and lasting impact of Pop Art on the art world and popular culture. What is Pop Art? Pop Art, short for "popular art," was a movement that emerged in the United States and the United Kingdom during the 1950s and 1960s. It was a reaction against the dominant abstract expressionist movement, which focused on subjective, introspective, and non-representational art. Pop Art, on the other hand, celebrated the ordinary, the commercial, and the mundane, drawing inspiration from mass-produced consumer goods, advertising, and popular culture. What are the characteristics of Pop Art? Appropriation and Repetition: Pop Art often incorporated images and objects taken from popular culture, such as product packaging, comic books, and celebrities. Artists manipulated and repeated these images to highlight their significance and challenge the concept of originality. Bold Colors and Simplified Forms: Pop artists used vibrant, eye-catching colors to attract attention and evoke a sense of consumerism. They simplified forms and employed graphic techniques, reminiscent of advertising and comic book aesthetics. Irony and Critique: Pop Art often conveyed a sense of irony and critique by juxtaposing disparate elements, subverting traditional art forms, and challenging societal norms. It questioned the boundaries between high and low culture, art and mass production, and the commercialization of society. Leading Artists of the Pop Art Movement Andy Warhol: One of the most iconic figures associated with Pop Art, Warhol employed screen-printing techniques to reproduce everyday objects, such as Campbell's soup cans and Coca-Cola bottles. His work explored themes of consumerism, fame, and the cult of celebrity. Roy Lichtenstein: Lichtenstein is renowned for his comic book-inspired paintings, featuring bold lines, Ben-Day dots, and speech bubbles. By appropriating and enlarging comic strip panels, he elevated popular culture to the realm of high art. Claes Oldenburg: Oldenburg's sculptures took ordinary objects and transformed them into monumental works of art. His oversized sculptures of hamburgers, typewriters, and clothespins challenged the viewer's perception of scale and materiality. Richard Hamilton: Considered the father of British Pop Art, Hamilton explored the relationship between art and technology. His collage-like works incorporated images from advertising, cinema, and popular magazines, reflecting the media-saturated society. Impact and Legacy Pop Art's influence extends far beyond its initial emergence in the 1960s. Its vibrant and accessible style has had a lasting impact on contemporary art, design, fashion, and popular culture. Pop Art paved the way for subsequent art movements such as Neo-Pop, Street Art, and the appropriation art of the 1980s. It blurred the boundaries between high and low art, challenged the traditional notions of artistic value, and emphasized the democratization of art. Concluding Remarks Pop Art revolutionized the art world by breaking away from the abstract and introspective tendencies of the time. It celebrated the everyday, the commercial, and the popular culture, making art more accessible to a wider audience. Through its use of appropriation, bold colors, and irony, Pop Art continues to captivate and inspire, leaving an indelible mark on contemporary art and popular culture.

ART 101
Exploring Art Medium: A Fusion of Category and Material in Art Creation
Art is a vast and diverse realm that encompasses a wide range of creative expressions. Within this realm, the concept of "Art Medium" holds a crucial role, serving as the bridge between artistic intent and tangible creation. The medium that an artist chooses to work with can have a significant impact on the style and meaning of the artwork. For example, a painting made with oil paints will have a different look and feel than a painting made with watercolors. In the context of Art attribution "Art Medium" has been used interchangeably to refer both the category of artwork and the materials used to bring forth an artist's vision. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of art medium, exploring its dual significance in the world of art. Art Medium as a Category of Art In its first sense, an art medium represents the various categories or disciplines within the field of art. Each medium possesses distinct characteristics, techniques, and artistic approaches. Let's explore some of the prominent art mediums: Painting: Painting is a traditional and widely recognized medium that employs pigments on surfaces such as canvas, paper, or wood. It encompasses various styles like oil painting, watercolor, acrylics, and mixed media, each offering unique visual qualities and expressive possibilities. Painting, Pop Horizon by Barron Holand Sculpture: Sculpture involves shaping and manipulating materials such as stone, wood, metal, clay, or even found objects. Artists create three-dimensional forms that can range from classical figurative representations to abstract and conceptual installations. Sculpture, S-04 BIG FOOT by Aleks Rosenberg Drawing: Drawing is a fundamental art medium that employs pencils, pens, charcoal, or other tools to create two-dimensional representations. It encompasses techniques like sketching, shading, and hatching, allowing artists to convey ideas, explore compositions, and develop their artistic skills. Drawing, Dancer in Red by NK Hong Photography: Photography born from the marriage of science and art, captures moments through the lens of a camera. It employs light-sensitive materials and digital technologies to immortalize scenes, people, and emotions, providing a unique perspective on the world. Photography, La grève Je T'aime by Gudzovsky Printmaking: Printmaking encompasses various techniques such as etching, lithography, screen printing, and relief printing. Artists create multiple copies of their artworks, each possessing its own subtle variations, by transferring images onto paper or other surfaces. Ceramics: Ceramics involves working with clay, shaping it into objects, and firing them in kilns to achieve hardness and permanence. This ancient medium encompasses functional pottery, decorative vessels, sculptures, and intricate porcelain works. Textiles: Textile art employs fabrics, threads, and fibers to create tactile and visually engaging works. It includes techniques like weaving, embroidery, quilting, and textile installations, exploring themes of culture, identity, and materiality. Installation and Performance Art:: These mediums go beyond traditional forms, embracing immersive experiences and the participation of the audience. Artists use various materials, space, sound, and movement to create site-specific installations or enact performances that challenge the boundaries of art. Digital NFT: Very recently Digital NFT is being regarded as an art medium, and more importantly revolutionising Digital Art representation. Utilizing blockchain technology, NFTs represent unique digital assets, such as artwork, music, or videos, providing a secure and verifiable link between the digital file and ownership rights. Art Medium as Material Used in Art Creation In the alternate context, an art medium refers to the specific materials and tools employed by artists to bring their artistic visions to life. The choice of medium significantly influences the aesthetic outcome and the creative process itself. Artists often use it to describe how they created their artwork, which gives a sense of how it needs to be viewed as well. For e.g. Oil paintings ( referenced as "Oil on Canvas") are best observed from a distance to get a more clearer understanding and the depth of the Art. Again depending on the Category of work there are different materials used to fulfill the Artistic vision of the creator. Here are some examples of art mediums in the context of Material Used Paints: Artists use various types of paints, including oil paints, watercolors, acrylics, and gouache, each with its own characteristics and techniques. These pigments, when combined with binders, allow artists to manipulate color, texture, and opacity on different surfaces. A combination of the paint type and the support used form the Medium used for the artwork, for e.g. Oil on Canvas, Gouache on paper, Acrylic on Linen etc... Drawing Tools: Pencils, pens, charcoal, markers, and pastels are all examples of drawing tools that artists employ. These tools vary in hardness, texture, and line quality, enabling artists to create intricate details or bold, expressive strokes. Sculpting Materials: Sculptors utilize a plethora of materials such as stone, wood, metal, clay, plastic, and even unconventional materials like ice or food. Each material offers its unique qualities, texture, and potential for manipulation. Cameras and Photographic Equipment: With the advent of photography, cameras and photographic equipment became vital art mediums. Film cameras, digital cameras, lenses, lighting equipment, and photo-editing software all contribute to the creation of photographic art. Printmaking Supplies: Printmaking relies on materials like printing plates, inks, brayers, and printing presses. These tools facilitate the transfer of images from the plate to the chosen substrate, resulting in distinct prints with their own visual characteristics. Clay and Kilns: Ceramics artists employ different types of clay, glazes, and firing techniques to shape and fire their creations. The firing process in kilns transforms the raw materials into durable and visually captivating ceramic pieces. Fabrics and Threads: Textile artists utilize a wide range of fabrics, threads, dyes, and surface design techniques to create intricate tapestries, clothing, quilts, or fiber-based sculptures. The choice of fabric and the application of techniques contribute to the overall visual and tactile impact of the artwork. The Importance of Art Medium The medium that an artist chooses to work with can have a significant impact on the style and meaning of the artwork. For example, a painting made with oil paints will have a different look and feel than a painting made with watercolors. The medium can also affect the way that the viewer interacts with the artwork, an example being, a sculpture that is made from metal will feel different to the touch than a sculpture that is made from wood. The art medium is of utmost importance in the representation of art as it influences the aesthetics, technical possibilities, symbolic significance, and cultural context of an artwork. It allows artists to express their vision, engage viewers, and communicate their intended messages effectively. The careful consideration and deliberate selection of the art medium contribute to the overall artistic expression and impact of the artwork.Different art mediums have evolved throughout history and across cultures, reflecting the societal and historical context in which they originated. The selection of a particular medium can evoke associations and references to specific art movements, traditions, or periods. The Future of Art Mediums The art world is constantly evolving, and new art mediums are being developed all the time. For example, digital art is becoming increasingly popular, as artists use computers and other digital tools to create their work. It is impossible to predict what the future holds for art mediums. However, it is likely that new art mediums will continue to be developed, and that artists will continue to experiment with different materials and techniques. It's important to note that the future of art mediums will be shaped by the creativity and experimentation of artists themselves, as they continue to push boundaries, embrace new technologies, and explore innovative approaches to art-making. The possibilities are vast, and the future of art mediums for visual artists holds exciting potential for artistic expression and engagement with audiences. Digital, Augmented and Virtual Realities, Mixed Media, Eco-Friendly Materials, BioArt and Living Materials, all are being explored, included and evolved for Artists to continously push the boundaries of their creative abilities to produce thought provoking artworks. Conclusion In the realm of art, the term "art medium" embraces a dual meaning. It encompasses both the categorization of art forms and the materials employed by artists. The category of art medium reflects the different disciplines and techniques artists employ to create their work, while the material aspect highlights the tangible tools and substances used to manifest their creative visions. Artists' choices of medium significantly influence the visual, tactile, and conceptual qualities of their artworks. Furthermore, contemporary artists often push the boundaries of traditional mediums by exploring hybrid forms and incorporating new technologies. Understanding the significance of art medium enhances our appreciation for the diverse expressions and the innovative approaches artists employ in their creative endeavors.








